5-4 Analyzing Graphs Of Polynomial Functions Worksheet With Answers Page 20
ADVERTISEMENT
5-4 Analyzing Graphs of Polynomial Functions
Sample answer: Sometimes it is necessary to have a more accurate viewing window or to change the interval values
of the table function in order to assess the graph more accurately.
48. REASONING The table below shows the values of g(x), a cubic function. Could there be a zero between x = 2 and
x = 3? Explain your reasoning.
SOLUTION:
Sample answer: No; the cubic function is of degree 3 and cannot have any more than three zeros. Those zeros are
located between –2 and –1, 0 and 1, and 1 and 2.
50. CCSS ARGUMENTS Determine whether the following statement is sometimes, always, or never true. Explain
your reasoning.
For any continuous polynomial function, the y-coordinate of a turning point is also either a relative
maximum or relative minimum.
SOLUTION:
Sample answer: Always; the definition of a turning point of a graph is a point in which the graph stops increasing and
begins to decrease, causing a maximum or stops decreasing and begins to increase, causing a minimum.
52. REASONING A function is said to be odd if for every x in the domain, –f (x) = f (–x). Is every odd-degree
polynomial function also an odd function? Explain.
SOLUTION:
3
2
Sample answer: No; f (x) = x
+ 2x
is an odd degree, but
.
2
54. Which of the following is the factorization of 2x – 15 + x
?
A . (x – 3)(x – 5)
B. (x – 3)(x + 5)
C. (x + 3)(x – 5)
D . (x + 3)(x + 5)
SOLUTION:
First rewrite the equation with the terms in descending order by degree. Then factor.
The correct choice is B.
2
56. Which polynomial represents (4x
+ 5x – 3)(2x – 7)?
3
2
F 8x
– 18x
– 41x – 21
3
2
G 8x
+ 18x
+ 29x – 21
3
2
H 8x
– 18x
– 41x + 21
3
2
J 8x
+ 18x
– 29x + 21
SOLUTION:
eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero
Page 20
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13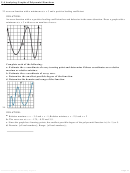 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23