Molecular Shapes Computer Modeling Lab Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
Data Analysis:
Using the data above, generate a sequential chart from the simplest molecule shape to the most
complex that indicates a relationship between bonded atoms to the central atom and lone pairs on
the central atom. Do not include redundant molecular shapes!
Use the following table as a guide:
Table I – Molecular Analysis
Number of
Number of
Total Number
Shape Name
Bond Angle(s)
Example
Atoms Bonded
Lone Pairs
of Attachments
Molecule
to Central
(Nonbonding
(electron
Atom
pairs) of
domains) on
electrons on
the Central
Central Atom
Atom
2
1
3
Bent
120°
SO
2
Conclusions:
1. State in your own words the basic idea of VSEPR theory?
2. How does VSEPR relate to the different molecular shapes?
3. Examine the NH
molecule. If you analyze this molecule in two dimensions (as you have it drawn
4 +
on your paper) what bond angle and shape seems to be present? How does the actual molecule
shape and bond angle appear (based on the computer model…which is 3-D)? Explain.
4. The modeling program allows you to place either bonded electrons or nonbonding electrons
around a central atom. You “built” a molecule with four single bonds and examined the bond angle
in the procedure #4 above and then removed one of the bonded atoms and replace it with a
nonbonding pair and recorded the angle.
(a) You examined the size of the electron orbital for a bonded pair of electrons with the size of the
orbital of a nonbonding pair…what did you notice? Explain this answer.
(b) The computer modeling program is actually incorrect on the bond angle for the molecule with
three bonded pairs and one nonbonding pair (the “Real Molecules” tab is correct). Would you
expect the bond angle between bonding pairs to increase or decrease when the nonbonding pair is
placed for a bonding pair? Explain. Examine your data from procedure #6 for the “corrected bond
angles” for some of the molecules.
5. CH
Cl is a 5 atom molecule and is a perfect tetrahedron, but AsCl
, also a 5 atom molecule, is
4 -
3
given a different shape name. Explain.
6. BeCl
and TeCl
are both covalent molecules, yet BeCl
is linear while TeCl
is nonlinear (bent).
2
2
2
2
Explain.
7. “In molecules or polyatomic ions that contain nonbonding pairs of valence electrons on the
central atom, the electronic geometry and the molecular geometry cannot be the same. Explain
this statement using your observations from procedure step #5.
8. Distinguish between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds. Define polar vs nonpolar molecules.
Examine the Lewis Dot diagrams for Cl
and HCl…both are linear, two atom molecules.
2
(a) Designate the more electronegative atom in HCl. Indicate the direction the shared pair of
electrons will be more tightly held and appropriately place a (+) and (-) charge on the end of this
molecule. What about doing the same for Cl
? Explain.
2
(b) Now, compare BH
and NH
for polar molecule status. Explain.
3
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1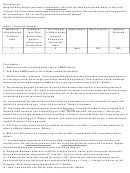 2
2








