Happy Atoms Worksheet Page 14
ADVERTISEMENT
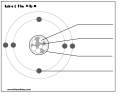
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
Big Idea
An element’s atomic structure and chemical properties determine the types of bonds that
element will form with other elements. Different numbers of valence electrons will cause
elements in the same period to have different properties. Elements in the same group will
have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons.
Learning Objectives
Students will be able to:
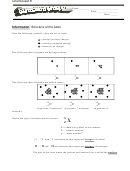
1. Visualize that the chemical properties of ionic and covalent compounds are caused
by their bond types. Students will demonstrate an understanding by identifying
similarities in compounds with ionic bonds, and differences when contrasting ionic
and covalent compounds.
2. Understand that elements in a period will have different chemical properties and
bonding types by identifying that elements across a period contain differing
numbers of valence electrons.
3. Understand that elements in a group will have similar chemical properties and
bonding types by identifying that elements within a group have the same number of
valence electrons.
Standards Addressed
1. Use the periodic table as a model to predict the relative properties of elements based on
the patterns of electrons in the outermost energy level of atoms. (HS-PS1-1.)
2. Science and Engineering Practice: Developing and using models
3. Crosscutting Concept: Structure and Function
Vocabulary, Content and Misconceptions
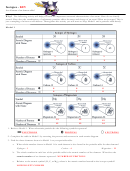
Ionic compound
Covalent compound
Cation
Anion
Students may try to break the octet rule with a group 5A, 6A, or 7A element because there
are many magnetic connectors with the Happy Atoms modeling set.
Single bonds modeled using Happy Atoms can be mistaken by students as double bonds
because there are two flexible arms involved. Since each atom is sharing one valence
electron (present at the end of each flexible arm), the atoms are only sharing one pair of
electrons, which is the definition of a single covalent bond.
There is a misconception that hydrogen will always make a covalent bond in a compound
because it is a nonmetal. Hydrogen, if acting as a hydride anion when paired with a metal
cation, will make an ionic bond.
Students may think that hydrogen can make more than a single bond. Students have tried
to create double or triple bonds to a hydrogen atom in a compound.
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33