Vsepr Theory Homework Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
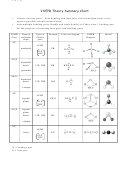
Geometry of Molecules
Rules for Drawing Lewis Structures
1. Count the total number of valence electrons in the
species. Remember to add electrons for anions and subtract
them for cations. (The number of valence electrons equals
the column number)
HCN
2. Express the total number as pairs by dividing the total by 2
2 Linear
2 0 Linear
180
N sp
CO
3. Arrange the atoms in the correct molecular skeleton.
2
[Many times the first element is the central. Try the element
that bonds the most (the number of bonds are indicated by
SO
2
3
3 trigonal
3 0 trigonal
120
N sp
-1
the valence of each column)]
NO
3
4. Place the pairs around the atoms so that each atom has
an octet, except H. Start by placing 1 pair between each
so
Angular
2
2
3 trigonal
2 1
<120
Y
sp
symbol.
-1
(bent)
NO
2
5. If an atom lacks an octet, consider double or triple bonds
between that atom and the adjacent atom.(Remember that
Halogens almost never form double bonds and H never
CH
3
4
N sp
4 tetrahedral 4 0 tetrahedral
109
+
does)
NH
4
6. The central atom may have an expanded octet (5 or 6
3
sp
pairs), but only if it is from the 3rd period or higher.
4 tetrahedral 3 1 pryamidal
<109
Y
NH
3
3
Some Hints for Complicated Ones
sp
4 tetrahedral 2 2 angular
<109
Y
H
O
Skeleton: Not much more than above. The lowest
2
electronegative element is usually in the middle. H is never
3
in the middle. Connect each atom to the central with a single
sp
d
trigonal
trigonal
5
5 0
120-90 N
PCl
5
bond(a line or a pair of electrons)
bipyramid
bipyramid
Number of electrons: Use the column number of each
3
sp
d
trigonal
teeter-
5
4 1
<120<90 Y
SF
element in the molecule to total the number of electrons in
4
bipyramid
totter
the molecule. For a Positive ion subtract the positive number
3
sp
d
trigonal
from the total. For a negative ion add the negative value to
5
3 2 T shaped
<90
Y
ClF
3
bipyramid
+1
the total. NH
= (5 + 1+1+1+1)-1
4
3
-1
sp
d
trigonal
ClO
= (7+6+6+6)+1
3
5
2 3 linear
180
N
XeF
2
bipyramid
Arranging Electrons: Deduct two valence electrons that are
used in each of the bonds in the skeleton. Distribute the
3
2
sp
d
remaining electrons as lone pairs so that each element has
6 octahedral 6 0 octahedral
90
N
SF
6
an octet. If there are too few electrons convert single bonds
to multiple bonds.(Double bonds are usually limited to bonds
3
2
sp
d
square
between C,N,O,S and maybe Se
6 octahedral 5 1
<90
Y
BrF
5
pyramid
Some atoms can't get 8 (B,Al) without extraordinary work.
3
2
Expanded Octets: If there are too many electrons (each
sp
d
element has an octet and there are some left) the central
square
6 octahedral 4 2
90
N
BrF
4
atom may have 10 or 12.(Will not happen to elements in the
planar
first or second row)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3