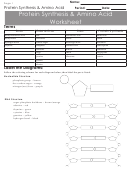
Amino Acids Peptides And Proteins Page 19
ADVERTISEMENT
1171
24-8
Structure and Nomenclature of Peptides and Proteins
peptide bond
O
O
FIGURE 24-6
Resonance stabilization of an amide
C
R
C
R
accounts for its enhanced stability,
R
N
R
N
the weak basicity of the nitrogen
atom, and the restricted rotation of
H
H
the
C ¬ N
bond. In a peptide, the
amide bond is called a peptide bond.
It holds six atoms in a plane: the C
and O of the carbonyl, the N and its
amide plane
H, and the two associated
a
carbon
atoms.
character and restricted rotation of an amide bond. In a peptide, this partial double-
bond character results in six atoms being held rather rigidly in a plane.
Having both an amino group and a carboxyl group, an amino acid is ideally suited
to form an amide linkage. Under the proper conditions, the amino group of one mole-
cule condenses with the carboxyl group of another. The product is an amide called a
dipeptide because it consists of two amino acids. The amide linkage between the
amino acids is called a peptide bond. Although it has a special name, a peptide bond
is just like other amide bonds we have studied.
peptide bond
2
2
O
O
R
H
R
H
+
+
H
N
C
C
H
N
C
C
3
3
+
loss of H
O
−
−
C 9 O
2
C 9 O
C
OH
H
N
C
N
3
1
1
H
R
H
R
H
O
O
In this manner, any number of amino acids can be bonded in a continuous chain.
A peptide is a compound containing two or more amino acids linked by amide bonds
between the amino group of each amino acid and the carboxyl group of the neighbor-
ing amino acid. Each amino acid unit in the peptide is called a residue. A polypeptide
is a peptide containing many amino acid residues but usually having a molecular
weight of less than about 5000. Proteins contain more amino acid units, with molecu-
lar weights ranging from about 6000 to about 40,000,000. The term oligopeptide is
occasionally used for peptides containing about four to ten amino acid residues.
Figure 24-7 shows the structure of the nonapeptide bradykinin, a human hormone that
helps to control blood pressure.
N terminus
C terminus
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
+
−
H
N
CH
C
N
CH
C
N
CH
C
NH
CH
C
NH
CH
C
NH
CH
C
N
CH
C
NH
CH
C
NH
CH
C
O
3
H
CH
CH
CH
2
2
2
NH
NH
OH
C
C
+
+
H
N
NH
H
N
NH
2
2
2
2
Arg
Pro
Pro
Gly
Phe
Ser
Pro
Phe
Arg
FIGURE 24-7
The human hormone bradykinin is a nonapeptide with a free
¬ NH
at its N terminus and a free
¬ COO
at its C terminus.
+
-
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5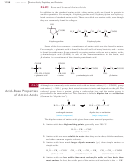 6
6 7
7 8
8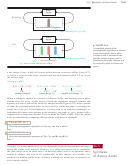 9
9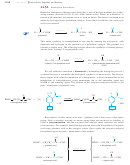 10
10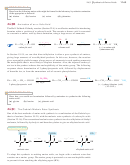 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16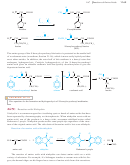 17
17 18
18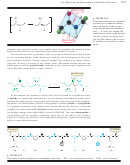 19
19 20
20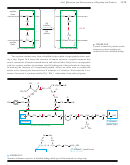 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25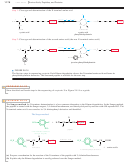 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31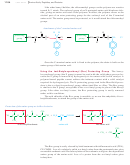 32
32 33
33 34
34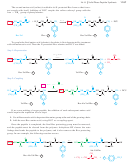 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47