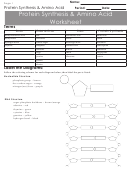
Amino Acids Peptides And Proteins Page 33
ADVERTISEMENT
1185
24-11
Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis
CH
O
CH
O
H
3
3
CF
COOH
3
CH
C
O
C
NH
CH
COOH
CH
C
O
C
NH
CH
COOH
3
3
CH
R
CH
R
3
3
Boc-amino acid
protonated
CH
O
H
CH
3
3
CH
C
O
C
NH
CH
COOH
H
N
CH
COOH
CH
C
CO
3
3
2
2
CH
CH
R
R
3
3
a carbamic acid
free amino acid
isobutylene
People who synthesize peptides generally do not make their own Boc-protected
amino acids. Because they use all their amino acids in protected form, they buy and
use commercially available Boc amino acids.
Use of DCC as a Peptide Coupling Agent
The final reaction needed for the
Merrifield procedure is the peptide bond-forming condensation. When a mixture of an
amine and an acid is treated with N,
N¿-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
(abbreviated DCC),
the amine and the acid couple to form an amide. The molecule of water lost in this
condensation converts DCC to N,
N¿-dicyclohexyl
urea (DCU).
O
O
O
H
H
R
C
O
H
N
R
N
C
N
R
C
NH
R
N
C
N
3
acid
amine
N,N -dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC)
amide
N,N -dicyclohexyl urea (DCU)
The mechanism for DCC coupling is not as complicated as it may seem. The car-
boxylate ion adds to the strongly electrophilic carbon of the diimide, giving an activated
acyl derivative of the acid. This activated derivative reacts readily with the amine to give
the amide. In the final step, DCU serves as an excellent leaving group. The cyclohexane
rings are miniaturized for clarity.
Formation of an activated acyl derivative
N
C
N
O
N
O
O
N
+
H
N
R
H 9 NH
9 R
2
2
R
C
O
R
C
O
C
R
C
O
C
N
NH
activated
Coupling with the amine and loss of DCU
O
O
N
O
N
O
N
R
C
NH
R
H
R
C
O
C
R
C
O
C
R
C
O
C
NH
NH
NH
N
amide
R
N
H
R
N
H
2
2
H
R
DCU
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5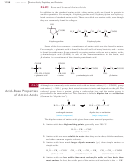 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9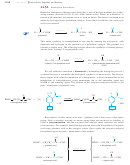 10
10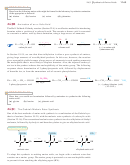 11
11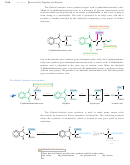 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16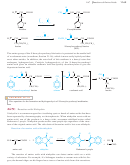 17
17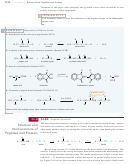 18
18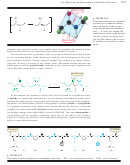 19
19 20
20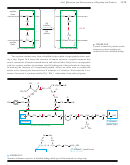 21
21 22
22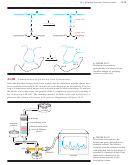 23
23 24
24 25
25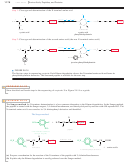 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31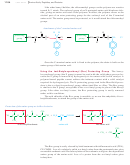 32
32 33
33 34
34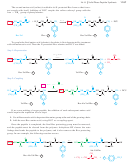 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45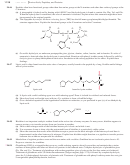 46
46 47
47