Covalent Bonding Chemistry Worksheets
ADVERTISEMENT
SCH3 U
Name:
COVALENT BONDING
This type of bond forms when a non-metal combines with another non-metal.
Since both non-metals have to gain electrons, they achieve this by sharing electrons either:
(i)
a single pair of electrons between them to form a single covalent bond
(ii)
a double pair of electrons between them to form a double covalent bond
(iii)
a triple pair of electrons between them to form a triple covalent bond
The non-metals share electrons such that they have 8 outer electrons when counting their own plus those "borrowed"
from the atoms bonding with them. The mutually share electrons.
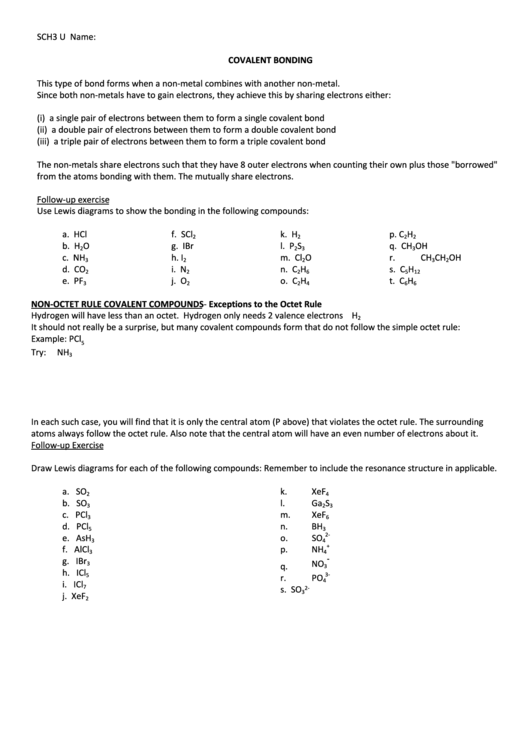
Follow-up exercise
Use Lewis diagrams to show the bonding in the following compounds:
a.
HCl
f.
SCl
k.
H
p.
C
H
2
2
2
2
b.
H
O
g.
IBr
l.
P
S
q.
CH
OH
2
2
3
3
c.
NH
h.
I
m.
Cl
O
r.
CH
CH
OH
3
2
2
3
2
d.
CO
i.
N
n.
C
H
s.
C
H
2
2
2
6
5
12
e.
PF
j.
O
o.
C
H
t.
C
H
3
2
2
4
6
6
NON-OCTET RULE COVALENT COMPOUNDS- Exceptions to the Octet Rule
Hydrogen will have less than an octet. Hydrogen only needs 2 valence electrons H
2
It should not really be a surprise, but many covalent compounds form that do not follow the simple octet rule:
Example: PCl
5
Try:
NH
3
In each such case, you will find that it is only the central atom (P above) that violates the octet rule. The surrounding
atoms always follow the octet rule. Also note that the central atom will have an even number of electrons about it.
Follow-up Exercise
Draw Lewis diagrams for each of the following compounds: Remember to include the resonance structure in applicable.
a.
SO
k.
XeF
2
4
b.
SO
l.
Ga
S
3
2
3
c.
PCl
m.
XeF
3
6
d.
PCl
n.
BH
5
3
2-
e.
AsH
o.
SO
3
4
+
f.
AlCl
p.
NH
3
4
-
g.
IBr
NO
3
q.
3
h.
ICl
3-
5
r.
PO
4
i.
ICl
7
s.
SO
2-
3
j.
XeF
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2








