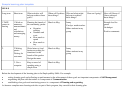
Sample Care Plan Template Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
8) Metabolic acidosis
8) Metabolic acidosis is a pH imbalance in
which the body has accumulated too much
acid and does not have enough bicarbonate to
effectively neutralize the effects of the acid
(McCance & Huether, 2010).
9) Transaminitis is a term for ↑ transaminases–
9) Transaminitis
AST, ALT, ALP coupled with non-specific
hepatitis (McCance & Huether, 2010). The
patient’s lab values on admission had
severely high AST, ALT, and ALP and a
diagnosis of mild hepatitis.
10) Cardiogenic shock
10) Cardiogenic shock occurs whenever the heart
is unable to pump as much blood as the body
needs. One of the common causes is a very
slow heart rhythm-bradycardia (“Cardiogenic
Shock”, 2012). Signs and symptoms are low
blood pressure with diastolic below 90 or
drops in BP greater than 10 mm Hg and weak
pulse (“Cardiogenic Shock”, 2012). This
patient was diagnosed with shock that was
induced by his sedation medication. The
reaction was severe enough that the patient
had to be placed on a continuous Levophed
drip while he is on the sedation medications.
This is complicating the patient’s recovery
and extubation.
11) Acute respiratory failure
11) Acute respiratory failure is when the blood
does not get enough oxygen from the lungs
(“What is respiratory failure”, 2012).
12) Aspiration pneumonia
12) Aspiration pneumonia is inflammation of the
lungs and airways to the lungs (bronchial
tubes) from breathing in foreign material
(McCance & Huether, 2010). The patient
aspirated on his vomit during the hospital
stay resulting in this diagnosis.
13) Alcohol dependence
13) Patient fits the clinical profile for chronic
alcohol abuse including withdrawal
symptoms, tolerance, and having an ongoing
desire to drink alcohol (“Alcoholism”, 2012).
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51