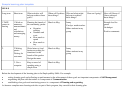
Sample Care Plan Template Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
(Katyal & Gajic, 2013). Type II’s etiological factors include: airway
failure due to obstruction/dysfunction, pneumothorax, and hemothorax
(Katyal & Gajic, 2013). Causes of type II ARF include: central
hypoventilation, COPD, asthma, and neuropathies.
Pulmonary diseases such as pneumonia can also lead to ARF. This
patient’s acute respiratory failure was caused by his aspiration
pneumonia. The patient had several of the risk factors for the
development of aspiration pneumonia. The patient had a decreased
LOC due to the medications for AWS treatment, GERD diagnosis, and
drinking large amounts of alcohol (“Aspiration Pneumonia”, 2012).
Alcoholics have pathophysiological changes that occur because of the
depression of the body’s natural defense mechanisms (Al-Sanouri,
Dikin, & Soubani, 2005). Alcohol can cause depression of normal
mucociliary function and hampers abilities of neutrophils and
macrophages (Al-Sanouri, Dikin, & Soubani, 2005). “Other inhibited
lower respiratory tract defenses include nonspecific antibacterial
activity of surfactant, opsonization by immunoglobulin or
complement, and intracellular killing by alveolar macrophages” (Al-
Sanouri, Dikin, & Soubani, 2005, p. 372). Finally, patients with
alcohol withdrawal syndrome can have diminished cough or reflexes
that lead to aspiration of materials. For this patient his aspiration
pneumonia developed when he aspirated his vomit.
References:
Al-Sanouri, I., Dikin, M., & Soubani, A.O. (2005). Critical care aspects of alcohol abuse. Southern Medical Journal 98(3): 372-381. Retrieved on
February 23, 2013, from
Katyal, P., & Gajic, O. (2013). Pathophysiology of respiratory failure and use of mechanical ventilation. Mayo Clinic Critical Care Clinical
Education. Retrieved on February 23, 2012, from
F:\group\MEPN\MEPN Level III\NURS610B\2013NURS 610B\610BCarePlan/12/17/2012
Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25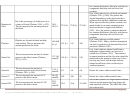 26
26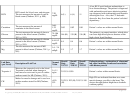 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51