Acids And Bases Worksheet With Answers Page 7
ADVERTISEMENT
46
CHAPTER 3
b) The highlighted proton is more acidic. When this location is deprotonated, the
conjugate base that is formed is stabilized by the electron-withdrawing effects of the
electronegative chlorine atoms, which are closer to this proton than the other proton:
O
Cl Cl
OH
HO
O
3.19.
a) The compound with two chlorine atoms is more acidic, because of the electron-
withdrawing effects of the additional chlorine atom, which help stabilize the conjugate
base that is formed when the proton is removed:
O
OH
Cl
Cl
b) The more acidic compound is the one in which the bromine atom is closer to the acidic
proton. The electron-withdrawing effects of the bromine atom stabilize the conjugate
base that is formed when the proton is removed:
O
OH
Br
3.20.
a) In the compound below, one of the chlorine atoms has been moved closer to the acidic
proton, which further stabilizes the conjugate base that is formed when the proton is
removed:
O
OH
Cl
Cl
b) In the compound below, one of the chlorine atoms has been moved farther away from
the acidic proton, which destabilizes the conjugate base that is formed when the proton is
removed:
Cl
O
Cl
OH
c) The compound below is less acidic than the compounds above, because this compound
is not a carboxylic acid. That is, the conjugate base of this compound is NOT resonance
stabilized:
Cl
Cl
OH
O
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2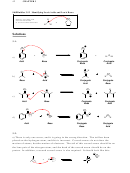 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7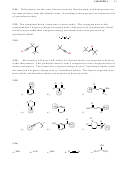 8
8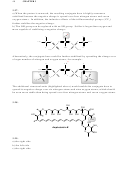 9
9 10
10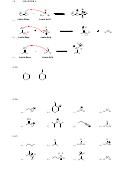 11
11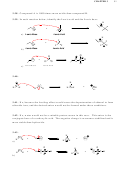 12
12 13
13 14
14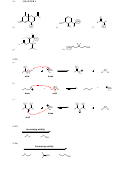 15
15 16
16 17
17








