Unit 1: Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis Economics Worksheet With Answers - Cma311s Notes, 2010 Page 20
ADVERTISEMENT
Activity 12
George Awarab recently opened a shop that specialises in car polish, a product that he has developed
himself. He has just received a diploma in accounting and is anxious to apply the principles he has learned at
the Polytechnic. As a first step, he has prepared the following analysis for his new store:
Sales price per tin
N$40
Variable costs per tin
16
Marginal income per tin
N$24
Fixed costs per year:
Rent on building
N$15 000
Depreciation on equipment
7 000
Selling expenses
20 000
Administrative expenses
18 000
Total fixed costs
N$60 000
Required:
12.1
Determine how many tins of polish must be sold each year in order to break even. What does this
represent in total N$ sales?
12.2
George has decided that he must earn at least N$18 000 during the first year to justify his time and
effort. Determine how many tins of polish he must sell to reach this target profit.
12.3
George now has a part-time sales person working in the store. It will cost him an additional N$8 000
per year to convert the part-time position to a full-time post. George believes that the change would
bring in an additional N$25 000 in sales each year. Determine whether he should convert the
position. Use the incremental approach (do not prepare an income statement).
12.4
Refer to the original data. During the first year, the store sold only 3 000 tins of polish and reported
the following operating results:
Sales (3 000 tins)
N$120 000
Less variable costs
48 000
Marginal income
72 000
Less fixed costs
60 000
Net income
N$ 12 000
12.4.1 Determine the store’s degree of operating leverage.
12.4.2 George is confident that with a more intense sales effort and with a more creative advertising
program he can increase sales by 50% next year. Determine what the expected percentage increase in
net income would be (use the degree of operating leverage to compute your answer).
Cost-volume-profit analysis assumptions
It is highly unlikely that selling price and variable costs per unit as well as fixed costs in total will remain
constant for a given period. Therefore, certain assumptions are part of break-even analysis. These
assumptions have given rise to criticism against CVP analysis. However, despite this criticism it remains a
useful management tool for short-term decision-making and profit planning.
Summary
CVP analysis is a useful tool with which to do certain short-term investigations and make decisions. It puts
an enterprise in a position to calculate its sales in order to make an expected profit level. It is therefore also
useful in evaluating the effect of operating changes on profit. These changes include changes in the selling
price and fixed costs. CVP analysis is liable to contain certain simplified assumptions that are necessary to
make the analysis clear and understandable.
20
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2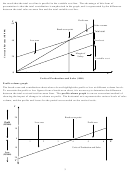 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13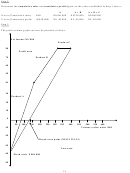 14
14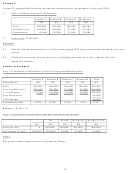 15
15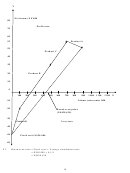 16
16 17
17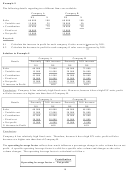 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27








