Unit 1: Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis Economics Worksheet With Answers - Cma311s Notes, 2010 Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
Expected profit after tax: Example 2
Easysteam Ltd manufactures and sells steam irons. The irons sell at N$190 per unit and the variable costs
amount to N$81,70 per unit. The company’s fixed costs are N$108 000 per year and the current tax rate is
35%.
Required:
Calculate what the company’s sales value (N$) must be if management expects a net income of N$125 000
after income tax.
Solution to Example 2
Fixed costs + [Expected after-tax profit ÷ (1 – Tax rate)]
Required sales value =
Marginal income ratio
N$108 000 + [N$125 000 ÷ (1 – 0,35)]
=
N$108,30 ÷ N$190
N$108 000 + (N$97 500 ÷ 0,65)
=
0,57
N$108 000 + N$192 308
=
0,57
N$300 308
=
0,57
= N$526 856
Activity 1:
A summary of a manufacturing company’s budgeted profit statement for its next financial year, when it
expects to be operating at 75% of capacity, is given below:
(N$)
(N$)
Sales 9 000 units at N$32
288 000
Less: Direct materials
54 000
Direct wages
72 000
Production overhead:
Fixed
42 000
Variable
18 000
186 000
Gross Profit
102 000
Less: Administration, selling
And distribution costs
Fixed
36 000
Varying with sales volume
27 000
63 000
Net profit
39 000
Required:
1.1
Calculate the break-even point in units and in N$-value
1.2
Draw a contribution (profit-volume) graph which indicates what profit could be expected if the
company operated at full capacity.
1.3
It has been estimated that:
1.3.1 if the selling price per unit were reduced to N$28, the increased demand would utilise 90% of the
company’s capacity without any additional advertising expenditure; and
4
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2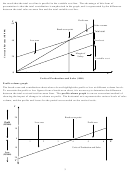 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13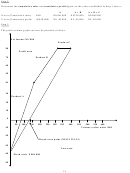 14
14 15
15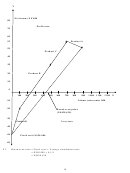 16
16 17
17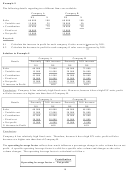 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27








