Operations And Algebraic Thinking Worksheets - Grade 4 Page 19
ADVERTISEMENT
Grade 4 Math Question Stem Bank:
C
C
S
S
o mmon
o re
t ate
t andards
Standards for Mathematical Practice
Represent and interpret data
.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.B.4
Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions of a unit (1/2, 1/4, 1/8). Solve problems involving addition and subtraction of
fractions by using information presented in line plots. F or example, from a line plot find and interpret the difference in length between the longest and shortest specimens in
an insect collection .
Geometric measurement: understand concepts of angle and measure angles.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.C.5
Recognize angles as geometric shapes that are formed wherever two rays share a common endpoint, and understand concepts of angle
measurement:
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.C.5
. A
An angle is measured with reference to a circle with its center at the common endpoint of the rays, by considering the
fraction of the circular arc between the points where the two rays intersect the circle. An angle that turns through 1/360 of a circle is called a "onedegree angle,"
and can be used to measure angles.
An angle that turns through n onedegree angles is said to have an angle measure of n degrees.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.C.5.B
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.C.6
Measure angles in wholenumber degrees using a protractor. Sketch angles of specified measure.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.C.7
Recognize angle measure as additive. When an angle is decomposed into nonoverlapping parts, the angle measure of the whole is
the sum of the angle measures of the parts. Solve addition and subtraction problems to find unknown angles on a diagram in real world and mathematical problems, e.g.,
by using an equation with a symbol for the unknown angle measure.
Geometry
Draw and identify lines and angles, and classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.G.A.1
Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular and parallel lines. Identify these in twodimensional
figures.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.G.A.2
Classify twodimensional figures based on the presence or absence of parallel or perpendicular lines, or the presence or absence of angles of a
specified size. Recognize right triangles as a category, and identify right triangles.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.G.A.3
Recognize a line of symmetry for a twodimensional figure as a line across the figure such that the figure can be folded along the line into
* It may be appropriate to read some of the longer problems out loud especially with lower readers
19
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13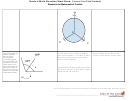 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21