Small Farm Business Planning Templates And Instrucitons Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
ii. Consider how you can adapt the farm plan to lessen seasonal cash flow problems.
Example: if you can grow vegetable starts inside and sell them early in the spring, it
will help generate cash to buy other necessary supplies needed at that time.
7.Time management plan
a. A time management plan is just like a cash flow plan only for hours instead of dollars.
You can also think of it as a time “budget’ . ’
i. Example: It simply cannot take three days to make your planting beds perfect,
because the only way to accomplish everything you need to do that week is to get
the beds done in 12 hours
ii. Example: If your farm plan says that you are going to use your tractor in February, you
need to make sure that you have time to buy the tractor in January or before. If you
plan to start selling at the farmers‘ market in April, you have to get your booth and
supplies together in March, as well as tending to your farming demands.
b. A time needs and availability analysis for the first two years of operations is necessary,
because the workload on a farm is not spread out evenly
c. The time analysis must match the cash flow worksheet and the farm plan
d. Develop a visual planner/calendar – Get a big calendar and list the major tasks in the
weeks that need to be accomplished, with an estimate of how long they should take
i. Schedule time for administration and marketing in every week
ii. Schedule driving to deliver orders and purchase supplies
iii. Schedule time to accomplish cultivation, harvest and packing tasks
iv. Do not schedule consecutive 105 hour work weeks—such a schedule is not
sustainable
e) Since you can’t “borrow” time, you will need to define how you will you manage a time deficit
D. Critical Elements of a Business Plan for the Development Phase
1. Complete in the start-up phase if possible, but realistically they will happen organically, out
of need as the business matures
2. Should stay on your mid-term list of things to do
3. Risk analysis
a. Identify risks (financial, production, marketing, legal and regulatory, family and personal)
b. Identify strategies to avoid or mitigate such risks
c. Plan on some setbacks occurring. If you are serious about staying in business you will
have some strategy for mitigating setbacks when things go wrong.
4. Plan for developing infrastructure
a. Infrastructure development plan – As your business grows it becomes more important
to have efficient systems for recordkeeping, internal communication, managing human
resources, etc. Usually these systems are developed in the first few years and then
improved as needs dictate.
b. Recordkeeping systems – Any system you develop to get you through the first few years
will need to be reviewed for efficiency and accuracy and updated and expanded as the
business grows
c. Internal communication and decision-making processes – As more people are added
this need will make itself known
d. Recruiting, training, and retaining assistance – When employees become a valuable
resource, it makes sense to invest in them through salary increases, benefits, housing, and
supplemental training
8 | Unit 2.0
Small Farm Business Planning
Lecture 1 Outline
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Business
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26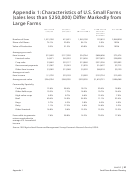 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36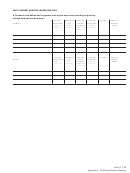 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50








