Dividends And Stock Valuation: A Study From The Nineteenth To The Twenty-First Century Page 14
ADVERTISEMENT
differences which may occur as a result of changes in inflation over time, we also include the change in
the level of the consumer price index (i.e., the rate of inflation), D_CPI.
PREM is estimated as the yield on a long-term AAA corporate bond less the yield on a long-term
government bond. This measure should capture changes in the business cycle. For example, when the
economy is doing poorly there should be greater market uncertainty and a higher default premium.
Consequently we might expect investors to be pessimistic and underestimate future dividends and/or
growth of dividends at this time. Thus we would expect this variable to be positively related to both UP1
and UP2 (i.e., the actual market price may be “too low” thus increasing the UPs at these times). TERM is
defined as the yield on long-term government bonds less the yield on short-term government bonds. This
measure is also designed to capture business cycle effects. A positive TERM or upward-sloping yield
curve is generally associated with economic expansion. Thus when the economy is doing poorly (a lower
or negative premium), we might expect investors to be pessimistic and underestimate future dividends
and/or the growth rate of dividends. Consequently we might expect this variable to be negatively related
to both UP1 and UP2 (i.e., the actual market price may be “too low” thus increasing the UPIs at these
times).
MOM is measured as the current price relative to the price five years previously. It is designed to
capture trends in the pricing of stocks. Consequently it should capture mis-pricings based on momentum
rather than fundamentals. When momentum is high, the actual prices may have become inflated so we
would expect this variable to be negatively related to both UP1 and UP2 (i.e., the actual market price may
be higher or above the “theoretical” prices thus decreasing the UPs). Finally, we consider the PE ratio
under the assumption that this measure will allow us to capture changes in how investors value earnings
over time. Studies of the changing value of the equity premium over time have suggested that one of the
major reasons for the dramatic changes in the value of the equity premium over the twentieth century is a
result of changes in how investors value earnings (e.g. Arnott and Bernstein (2002)). The expected price
may be too low at the times when the PE ratio is increasing and thus investors are valuing earnings more
12
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Business
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33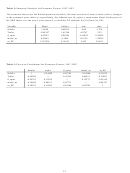 34
34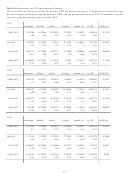 35
35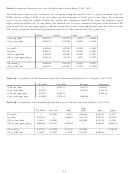 36
36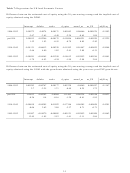 37
37 38
38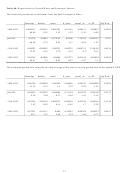 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45