Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chemistry Worksheet Page 10
ADVERTISEMENT
216
Chapter 6
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
3‒
The oxidation number for the phosphorus atom in PO
is always the same,
4
no matter what the cation is that balances its charge. Thus we could also have
determined the oxidation number of each phosphorus atom by considering
the phosphate ion separately from the calcium ion.
(ox # P) + 4(ox # O) = −3
(ox # P) + 4(
−
2) = −3
(ox # P) = +5
must have an oxidation number of +4.
The silicon atoms in CaSiO
3
(ox # Ca) + (ox # Si) + 3(ox # O) = 0
(+2) + (ox # Si) + 3(−2) = 0
(ox # Si) = +4
The oxidation numbers for the individual atoms in the first reaction are
below.
Oxidation number increases, oxidized
+2
+5
−2
+4 −2
0
0
+2
−2
+2
+4
−2
+ 6SiO
+ 10C
+ 10CO + 6CaSiO
2Ca
(PO
)
P
3
4
2
2
4
3
Oxidation number decreases, reduced
Phosphorus atoms and carbon atoms change their oxidation numbers, so
the reaction is redox. Each phosphorus atom changes its oxidation number
from +5 to zero, so the phosphorus atoms in Ca
(PO
)
are reduced, and
3
4
2
Ca
(PO
)
is the oxidizing agent. Each carbon atom changes its oxidation
3
4
2
number from zero to +2, so the carbon atoms are oxidized, and carbon is the
reducing agent.
b. Now, let’s consider the second reaction.
Combined oxygen, oxidation number −2
+ 5O
+ 6H
P
O
4H
PO
4
2
2
3
4
Pure elements,
Hydrogen in a molecular compound,
oxidation number +1
oxidation number 0
The following shows how we can determine the oxidation number of the
phosphorus atom in H
PO
:
3
4
3(ox # H) + (ox # P) + 4(ox # O) = 0
3(+1) + (ox # P) + 4(−2) = 0
(ox # P) = +5
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16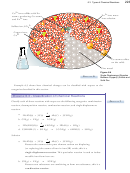 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41