Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chemistry Worksheet Page 24
ADVERTISEMENT
230
Chapter 6
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Chapter
Oxidation Any chemical change in which at least one element loses electrons, either
Glossary
completely or partially.
Reduction Any chemical change in which at least one element gains electrons, either
completely or partially.
Oxidation-reduction reactions The chemical reactions in which there is a complete
or partial transfer of electrons, resulting in oxidation and reduction. These reactions
are also called redox reactions.
Half-reactions Separate oxidation and reduction reaction equations in which electrons
are shown as a reactant or product.
Reducing agent
A substance that loses electrons, making it possible for another
substance to gain electrons and be reduced.
Oxidizing agent A substance that gains electrons, making it possible for another
substance to lose electrons and be oxidized.
Oxidation number A tool for keeping track of the flow of electrons in redox reactions
(also called oxidation state).
Combination or synthesis reaction The joining of two or more elements or compounds
into one product.
Decomposition reaction The conversion of one compound into two or more simpler
substances.
Combustion reaction Rapid oxidation accompanied by heat and usually light.
Single-displacement reaction
Chemical change in which atoms of one element
displace (or replace) atoms of another element in a compound.
Voltaic cell A system in which two half‑reactions for a redox reaction are separated,
allowing the electrons transferred in the reaction to be passed between them
through a wire.
Battery A device that has two or more voltaic cells connected together. The term is
also used to describe any device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy
using redox reactions.
Electrodes The electrical conductors placed in the half‑cells of a voltaic cell.
Anode The electrode at which oxidation occurs in a voltaic cell. It is the source of
electrons and is the negative electrode.
Cathode The electrode at which reduction occurs in a voltaic cell. It is the positive
electrode.
Salt bridge A device used to keep the charges in a voltaic cell balanced.
Electrolyte The portion of a voltaic cell that allows ions to flow.
Primary battery A battery that is not rechargeable.
Secondary battery or storage battery A rechargeable battery.
Electrolysis The process by which a redox reaction is pushed in the nonspontaneous
direction or the process of applying an external voltage to a voltaic cell, causing
electrons to move from what would normally be the cell’s cathode toward its
anode.
You can test yourself on the glossary terms at the textbook’s Web site.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16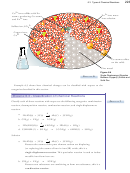 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41