Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chemistry Worksheet Page 22
ADVERTISEMENT
228
Chapter 6
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Nickel-Cadmium Batteries
Leclanché cells are not rechargeable; once the reactants are depleted, the battery must
be discarded and replaced. Batteries that are not rechargeable are called primary
batteries. A rechargeable battery is called a secondary battery or a storage battery.
The nickel‑cadmium (NiCd) battery is a popular rechargeable battery that uses the
following redox reaction:
Cd(s) + 2OH
‒
(aq) → Cd(OH)
(s) + 2e
‒
Anode reaction:
2
‒
Cathode reaction: NiO(OH)(s) + H
O(l ) + e
2
→ Ni(OH)
(s) + OH
‒
(aq)
2
Net Reaction: Cd(s) + 2NiO(OH)(s) + 2H
O(l )
2
→ Cd(OH)
(s) + 2Ni(OH)
(s)
2
2
To recharge a secondary battery, an opposing external voltage is applied that is
greater than the voltage of the cell, pushing the electrons in the opposite direction
from the way they move in the normal operation of the cell. In this process, the
original chemical reaction is reversed. Because the Cd(OH)
and Ni(OH)
produced
2
2
during the normal operation of the nickel‑cadmium battery are solids, they stay at the
electrodes where they are formed and are available to be converted back to the original
reactants.
normal operation
Cd(s) + 2NiO(OH)(s) + 2H
(s) + 2Ni(OH)
O(l )
Cd(OH)
(s)
2
2
2
when being charged
Leclanché cells and nickel‑cadmium batteries both have their drawbacks. One
problem with the Leclanché cell is that over time the zinc metal and the ammonium
ions react to corrode the anode, so dry cell batteries have a shorter “shelf life” than
other batteries do. Another problem is that Leclanché cells are not rechargeable.
Nickel‑cadmium batteries are rechargeable, but they are too bulky to be used for many
purposes. The manufacturers of electronic devices are constantly trying to make their
products smaller and more powerful. Thus they want batteries that are smaller, lighter,
and more powerful than dry cell and nickel‑cadmium batteries. They want batteries
with the highest possible energy‑to‑mass ratio and energy‑to‑volume ratio, and dry
cells and NiCd batteries have very low ratios. To solve these and other problems, many
additional types of batteries have been developed, including the lithium battery (Table
7.3).
Extensive research is being done to develop new types of batteries to power electric
cars and trucks. See Special Topic 6.3 Zinc-Air Batteries for an example.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16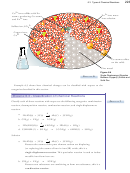 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41