Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chemistry Worksheet Page 28
ADVERTISEMENT
234
Chapter 6
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Complete the following statements by writing one of these words or phrases in each
blank.
chemical energy
not rechargeable
electrical conductors
oxidation
electrical energy
positive
electrolysis
positive electrode
flow
rechargeable
force
reduction
half‑reactions
voltaic cells
21.
Strictly speaking, a battery is a series of _____________ joined in such a way
that they work together. A battery can also be described as a device that converts
_____________ into _____________ using redox reactions.
22. A voltaic cell keeps two oxidation‑reduction _____________ separated, causing
the electrons released in the oxidation half of the reaction to pass through a wire
connecting the two halves of the apparatus.
23.
Metal strips in voltaic cells are called electrodes, which is the general name for
_____________ placed in half‑cells of voltaic cells.
24. The electrode at which _____________ occurs in a voltaic cell is called the
anode. Because electrons are lost, forming more positive (or less negative) species
at the anode, the anode surroundings tend to become more _____________.
25.
The cathode is the electrode in a voltaic cell at which _____________ occurs.
By convention, the cathode is designated the _____________. Because electrons
flow along the wire to the cathode, and because substances gain those electrons
to become more negative (or less positive), the cathode surroundings tend to
become more negative. Thus cations are attracted to the cathode.
26. The component of the voltaic cell through which ions are able to
_____________ is called the electrolyte.
27.
Voltage, a measure of the strength of an electric current, represents the
_____________ that moves electrons from the anode to the cathode in a voltaic
cell. When a greater voltage is applied in the opposite direction, electrons can be
pushed from what would normally be the cathode toward the voltaic cell’s anode.
This process is called _____________.
28. Batteries that are _____________ are called primary batteries. A(n)
_____________ battery is called a secondary battery or a storage battery.
Chapter
Section 6.1 An Introduction to Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Problems
29. Describe the difference between the redox reactions that form binary ionic
compounds, such as zinc oxide, from their elements and the similar redox
O
3
bjeCtive
reactions that form molecular compounds, such as nitrogen monoxide, from their
elements.
30.
Are the electrons in the following redox reactions transferred completely from
the atoms of one element to the atoms of another or are they only partially
transferred?
a. 4Al(s) + 3O
(g) → 2Al
O
(s)
2
2
3
b. C(s) + O
(g) → CO
(g)
2
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16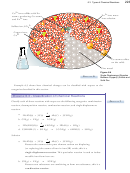 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41