Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chemistry Worksheet Page 14
ADVERTISEMENT
220
Chapter 6
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
added to natural gas to give the otherwise odorless gas a smell that can be detected in
case of leaks (Figure 6.3).
SH(g) + 3O
( g) → CO
(g) + 2H
O(l ) + SO
CH
(g)
3
2
2
2
2
Figure 6.3
sulfur atom
Odor of Natural Gas
The methane thiol added to natural gas
warns us when there is a leak.
The following sample study sheet lists the steps for writing equations for combustion
reactions.
Sample Study
Tip-off You are asked to write an equation for the complete combustion of a substance
composed of one or more of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur.
Sheet 6.2
General Steps
Writing
Step 1 Write the formula for the substance combusted.
Equations for
Step 2 Write O
(g) for the second reactant.
2
Combustion
Step 3 Predict the products using the following guidelines.
Reactions
a. If the compound contains carbon, one product will be CO
(g).
2
b. If the compound contains hydrogen, one product will be H
O(l ).
2
O
8
bjeCtive
(Even though water may be gaseous when it is first formed
in a combustion reaction, we usually describe it as a liquid in
the equation. By convention, we usually describe the state of
each reactant and product as their state at room temperature
and pressure. When water returns to room temperature, it is a
liquid.)
c. If the compound contains sulfur, one product will be SO
(g).
2
d. Any oxygen in the combusted substance would be distributed
between the products already mentioned.
Step 4 Balance the equation.
Example See Example 6.2.
e
6.2 - Combustion Reactions
xample
Write balanced equations for the complete combustion of (a) C
H
(l ),
O
8
bjeCtive
8
18
(b) CH
OH(l ), and (c) C
H
SH(l ).
3
3
7
Solution
a. The carbon in C
H
goes to CO
(g), and the hydrogen goes to H
O(l ).
8
18
2
2
(g) → 16CO
2C
H
(l ) + 25O
(g) + 18H
O(l )
8
18
2
2
2
b. The carbon in CH
OH goes to CO
(g), the hydrogen goes to H
O(l ), and
3
2
2
the oxygen is distributed between the CO
(g) and the H
O(l ).
2
2
(g) → 2CO
2CH
OH(l ) + 3O
(g) + 4H
O(l )
3
2
2
2
c. The carbon in C
H
SH goes to CO
( g), the hydrogen goes to H
O(l ), and
3
7
2
2
the sulfur goes to SO
(g).
2
(g) → 3CO
C
H
SH(l ) + 6O
( g) + 4H
O(l ) + SO
(g)
3
7
2
2
2
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16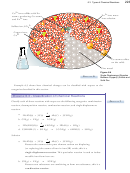 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41