Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chemistry Worksheet Page 17
ADVERTISEMENT
223
6.3 Types of Chemical Reactions
2+
Cu
ions collide with Zn
2+
Zn
ions move
atoms, producing Cu atoms
2+
2−
into solution.
2+
2−
2+
and Zn
ions.
2+
2-
2+
2+
2-
2+
2−
Sulfate ion, SO
4
2-
−
2−
2e
2+
2+
Copper ions,
2−
2+
2+
Cu
2-
2-
2+
2+
2+
2-
2-
2-
2-
2+
2-
2+
2+
2−
2+
500
2+
400
Cu atoms collect
2−
300
on the solid.
200
100
Zinc metal
Figure 6.4
Single-Displacement Reaction
O
9
bjeCtive
Between Copper(II) Sulfate and
Solid Zinc
Example 6.3 shows how chemical changes can be classified with respect to the
categories described in this section.
e
6.3 - Classification of Chemical Reactions
xample
Classify each of these reactions with respect to the following categories: combination
O
7
bjeCtive
reaction, decomposition reaction, combustion reaction, and single‑displacement
reaction.
∆
a. 2Fe
O
(s) + 3C(s)
4Fe(l ) + 3CO
( g)
2
3
2
(g) + F
(g) → 2ClF(g)
b. Cl
2
2
∆
c. 2Pb(NO
( g) + 2PbO(s) + O
)
(s)
4NO
(g)
3
2
2
2
SH(l ) + 9O
(g) → 5CO
(g) + 6H
O(l ) + SO
d. C
H
(g)
5
11
2
2
2
2
Solution
∆
a. 2Fe
O
(s) + 3C(s)
4Fe(l ) + 3CO
( g)
2
3
2
Because the atoms of the pure element carbon are displacing
(or replacing) the atoms of iron in iron(III) oxide, this is a
single‑displacement reaction. This particular reaction is used to isolate
metallic iron from iron ore.
(g) + F
(g) → 2ClF(g)
b. Cl
2
2
Because two substances are combining to form one substance, this is a
combination reaction
.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16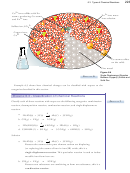 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41