Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chemistry Worksheet Page 13
ADVERTISEMENT
219
6.3 Types of Chemical Reactions
Decomposition Reactions
In decomposition reactions, one compound is converted into two or more simpler
O
7
bjeCtive
substances. The products can be either elements or compounds. For example, when
an electric current is passed through liquid water or molten sodium chloride, these
compounds decompose to form their elements.
Electric current
( g ) + O
2H
O(l )
2H
( g)
2
2
2
Electric current
2Na(l ) + Cl
2NaCl(l )
( g)
2
Another example is the decomposition of nitroglycerin. When this
compound decomposes, it produces large amounts of gas and heat, making
nitroglycerin a dangerous explosive.
(l ) → 12CO
(g) + 6N
(g) + 10H
O(g) + O
4C
H
N
O
(g)
3
5
3
9
2
2
2
2
As is true of combination reactions, not all decomposition reactions are redox
reactions. The following equation represents a decomposition reaction that is
not a redox reaction.
Dynamite, which has nitroglycerine
∆
as its active component, can be used
CaO(s) + CO
CaCO
(s)
(g)
3
2
to blast tunnels through solid rock.
Combustion Reactions
A log burns in the fireplace as a result of a combustion reaction, a redox reaction
O
7
bjeCtive
in which oxidation is very rapid and is accompanied by heat and usually light. The
combustion reactions that you will be expected to recognize have oxygen, O
, as one
2
of the reactants. For example, the elements carbon, hydrogen, and sulfur react with
oxygen in combustion reactions.
C(s) + O
(g) → CO
(g)
2
2
(g) + O
(g) → 2H
2H
O(l )
2
2
2
(s) + 8O
(g) → 8SO
S
( g)
8
2
2
When any substance that contains carbon is combusted (or burned) completely,
O
8
bjeCtive
the carbon forms carbon dioxide. When a substance that contains hydrogen is burned
completely, the hydrogen forms water. Therefore, when hydrocarbons
found in natural gas, gasoline, and other petroleum products burn
completely, the only products are CO
and H
O. The equations below
2
2
represent the combustion reactions for methane, the primary component
of natural gas, and hexane, which is found in gasoline.
(g) + 2O
(g) → CO
(g) + 2H
CH
O(l )
4
2
2
2
(l ) + 19O
(g) → 12CO
(g) + 14H
2C
H
O(l )
6
14
2
2
2
The complete combustion of a substance, such as ethanol, C
H
OH,
2
5
that contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen also yields carbon dioxide
Combustion reactions include oxygen as
and water.
a reactant and are accompanied by heat
and usually light.
OH(l ) + 3O
(g) → 2CO
(g) + 3H
C
H
O(l )
2
5
2
2
2
When any substance that contains sulfur burns completely, the sulfur forms sulfur
O
8
bjeCtive
dioxide. For example, when methanethiol, CH
SH, burns completely, it forms carbon
3
dioxide, water, and sulfur dioxide. Small amounts of this strong‑smelling substance are
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16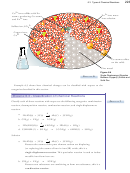 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41