Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Chemistry Worksheet Page 34
ADVERTISEMENT
240
Chapter 6
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
61.
The following pairs react in single‑displacement reactions that are similar to the
O
9
bjeCtive
reaction between uncharged zinc metal and the copper(II) ions in a copper(II)
sulfate solution. Describe the changes in these reactions, including the nature
of the particles in the system before the reaction takes place, the nature of the
reaction itself, and the nature of the particles in the system after the reaction.
Your description should also include the equations for the half‑reactions and the
net ionic equation for the overall reaction.
a.
Magnesium metal and nickel(II) nitrate, Ni(NO
)
(aq)
3
2
b. Calcium metal and cobalt(II) chloride, CoCl
(aq)
2
Section 6.4 Voltaic Cells
62.
We know that the following reaction can be used to generate an electric current
O
10
bjeCtive
O
11
bjeCtive
in a voltaic cell.
Zn(s) + CuSO
(aq) → Cu(s) + ZnSO
(aq)
4
4
Sketch similar voltaic cells made from each of the reactions presented below,
showing the key components of the two half‑cells and indicating the cathode
electrode and the anode electrode, the negative and positive electrodes, the
direction of movement of the electrons in the wire between the electrodes, and
the direction of movement of the ions in the system. Show a salt bridge in each
sketch, and show the movement of ions out of the salt bridge.
Mn(s) + Pb(NO
(aq) → Pb(s) + Mn(NO
a.
)
)
(aq)
3
2
3
2
b. Mg(s) + 2AgNO
(aq) → 2Ag(s) + Mg(NO
)
(aq)
3
3
2
63.
The following equation summarizes the chemical changes that take place in a
O
3
bjeCtive
O
4
bjeCtive
typical dry cell.
O
5
bjeCtive
+
Zn(s) + 2MnO
(s) + 2NH
(aq)
O
6
2
4
bjeCtive
→ Zn
2+
(aq) + Mn
(s) + 2NH
(aq) + H
O
O(l )
2
3
3
2
Determine the oxidation number for each atom in the equation, and identify
what is oxidized, what is reduced, the oxidizing agent, and the reducing agent.
64. The following equation summarizes the chemical changes that take place in a
O
3
bjeCtive
O
4
nickel‑cadmium battery. Determine the oxidation number for each atom in the
bjeCtive
O
5
bjeCtive
equation, and identify what is oxidized, what is reduced, the oxidizing agent, and
O
6
bjeCtive
the reducing agent.
Cd(s) + 2NiO(OH)(s) + 2H
O(l ) → Cd(OH)
(s) + 2Ni(OH)
(s)
2
2
2
65.
The following equation summarizes the chemical changes that take place in
O
3
bjeCtive
O
4
bjeCtive
a lead‑acid battery. Determine the oxidation number for each atom in the
O
5
bjeCtive
equation, and identify what is oxidized, what is reduced, the oxidizing agent, and
O
6
bjeCtive
the reducing agent.
+
‒
Pb(s) + PbO
(s) + 2HSO
(aq) + 2H
(aq) → 2PbSO
(s) + 4H
O
O(l )
2
4
3
4
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16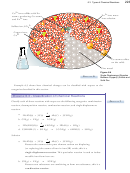 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41