Quality Assurance Project Plan Including Sampling And Analysis Plan Page 19
ADVERTISEMENT
Hunters Point Shipyard Parcel F ESTCP Demonstration Plan
Appendix A: Quality Assurance Project Plan
A.2.4.2 Assessment of Reductions in Aqueous PCB Availability and PCB Bioaccumulation
To determine that the AC treatments lead to a reduction in aqueous PCB availability and PCB
bioaccumulation, the following assessments will be completed during the course of the ESTCP DP
project:
a) PCB bioaccumulation in test clams and indigenous amphipods retrieved from plots (ERDC),
b) AC treatment effects on indigenous benthic community structure (ERDC), and
c) in situ PCB stabilization using physicochemical tests of PCB availability (Stanford/UMBC).
Further details of these field sampling and analysis methods associated with the above assessments are
provided in Sections A.3.2 through A.3.5.
A.2.4.3
Assessment of Resuspension Potential
The overlying water above the five plots will be sampled during high tide once before and thrice after
treatments to evaluate possible sediment and PCB resuspension and measure suspended and dissolved
PCB concentrations. The sampling and analysis methods associated with this assessment are provided in
Sections A.3.2 through A.3.5.
A.2.5
Quality Objectives and Criteria
A.2.5.1
Data Quality Objectives
The development of the DQOs for the ESTCP DP followed U.S. EPA’s Guidance for the Data Quality
Objectives Process (U.S. EPA QA/G-4, 2000b). The DQOs have been divided into two categories that
relate to those defined in the ESTCP DP. The DQOs for primary quantitative performance criteria are
defined in Table A-2; the DQOs for secondary performance criteria are defined in Table A-3. Table A-4
defines the measurements that will be completed to assess the primary performance criteria and secondary
performance for the ESTCP DP. Measurements that will be done by BDO on the archived sample splits
and will produce critical data for the Navy are identified Table A-4.
A.2.5.2
Measurement Quality Objectives
Measurement quality objectives for critical analyses conducted for this study can be expressed in terms of
accuracy, precision, completeness, and sensitivity goals. Accuracy and precision are monitored through
the analysis of QC samples (Section A.3.5). Completeness is a calculated value. Sensitivity is monitored
through instrument calibration (Section A.3.7) and the determination of method detection limits (MDLs)
and reporting limits (Section A.2.5.2). Qualitative quality objectives, expressed in terms of comparability
and representativeness, are addressed as part of the sampling design.
Accuracy is defined as the degree of agreement between an observed value and an accepted
reference value. Accuracy includes a combination of random error (precision) and systematic
error (bias) components that are due to sampling and analytical operations.
Precision is defined as degree to which a set of observations or measurements of the same
property, obtained under similar conditions, conform to themselves. Precision is usually
expressed as standard deviation, variance, or range, in either absolute or relative terms.
Completeness is the amount of data collected as compared to the amount needed to ensure that
the uncertainty or error is within acceptable limits. The goal for data completeness is 100%.
Page A-
19
of A-67
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Business
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27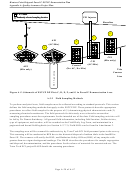 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61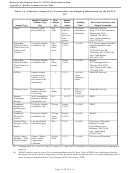 62
62 63
63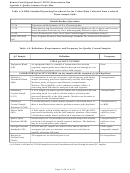 64
64 65
65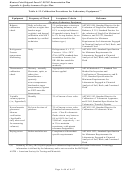 66
66 67
67








