Quality Assurance Project Plan Including Sampling And Analysis Plan Page 57
ADVERTISEMENT
Hunters Point Shipyard Parcel F ESTCP Demonstration Plan
Appendix A: Quality Assurance Project Plan
Table A-2. Data Quality Objectives for Primary Quantitative Performance Criteria of ESTCP DP
(continued)
STEP 7: Optimize the Design for Obtaining Data
PCB Bioaccumulation in Test Clams
PCB bioaccumulation will be measured using Macoma nasuta clams that are particle-feeding organisms native
to San Francisco Bay. Six clams will be deployed into each of the five mesh-covered clam tubes that are sunk
into the five random sampling locations of each plot as shown in Figure A-5. At three intervals during the study
(1 month pre-treatment, 6 months post-treatment, and 18 months post-treatment), we will deploy clams and
characterize their survival and 28-day PCB bioaccumulation. To measure PCB bioaccumulation, living clams
shall be removed from tubes and transferred to a vented polyethylene jar that contains clean water. The clams
will be transported to Stanford University and allowed to depurate in clean water for 48 hours at ambient
temperatures. After depuration, each surviving clam will be shucked and each resulting clam tissue will be
placed into a separate pre-cleaned 20 mL scintillation vial. The vials containing a single clam tissue will be
immediately placed in a -10°C freezer. Once frozen, the samples will be shipped overnight (on dry ice in a
cooler) to ERDC. At ERDC each set of six (or total number surviving) clams that came from a given clam tube
will be homogenized and split. Half will be shipped to BDO for archival at -10°C; while the other half will be
analyzed at ERDC. the clams will be removed from the field after exposure and depurated in clean sediment for
48 hr. The clams will then be subjected to PCB congener, moisture and lipid analyses.
PCB Bioaccumulation in Indigenous Amphipods
PCB bioaccumulation will be measured in indigenous benthic biota. At each the three sampling time points,
five separate surface (0-2 cm) sediment samples shall be collected at the five random sampling locations in each
plot as shown in Figure A-5, and placed into a separate wide-mouthed polyethylene jar with a vented lid. These
jars shall be maintained at <18 °C in a cooler, and transferred to laboratory conditions within 2h of collection
where they will be sieved for Corophium spp.amphipods. Each sieved sediment sample shall provide at least
200 mg wet weight of amphipods. In the laboratory, the amphipods shall be removed from the sediment using a
500µm sieve and rinsed with clean artificial seawater. Amphipods shall be depurated for 24 h using San
Francisco Bay seawater receiving trickle flow aeration in a cold room facility at 15 °C. Following depuration,
amphipods from each sampling location shall be removed and weighed by placing them into tarred and pre-
cleaned 20 mL scintillation vials. Samples will be immediately frozen. Once frozen, samples will be shipped on
dry ice to ERDC for homogenization and splitting. Half of the resulting homogenate sample will be analyzed by
ERDC, while the other half will be shipped on dry ice to BDO for archival at -10°C. Analysis of the PCB
concentrations in these amphipod samples will assess the AC treatment effects upon PCB bioaccumulation
in a resident benthic population.
Depth and Homogeneity of the Mixed AC
In each plot, 2.0-inch-diameter sediment core samples will be collected at five randomly distributed sampling
locations once before and twice after plot treatments. Each of the core samples collected will be one foot in
length (minimum) and divided into 2-inch-long core cross sections. A direct correlation exists between
measured TOC and the amount of AC added in sediment, so TOC analysis will be performed on a subsample of
each core section to evaluate the degree of AC mixing into sediment.
Resuspension of PCBs
Duplicate samples of the overlying water above the five plots during high tide once before and thrice after plot
treatments will take place to measure the dissolved and particulate PCB concentrations. A total of 40 water
samples will be collected 0.5 foot above the sediment surface for. Sample collection involves pumping water
through a pre-combusted glass fiber filter with a nominal pore size of 0.7 microns in a stainless steel filter
holder to trap suspended particles; this will be followed by passing the filtered water through a XAD-2 resin
trap in a glass column.
Page A-
57
of A-67
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Business
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27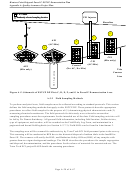 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61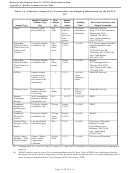 62
62 63
63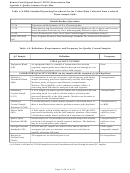 64
64 65
65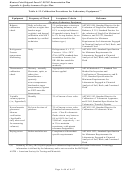 66
66 67
67








