Aircraft Accident Brief Ntsb/aab-02/01 (Pb2002-910401): Egypt Air Flight 990, Boeing 767-366er, Su-Gap - National Transportation Safety Board Page 23
ADVERTISEMENT
 1
1  2
2  3
3  4
4  5
5  6
6  7
7  8
8  9
9  10
10  11
11  12
12  13
13  14
14  15
15  16
16  17
17  18
18  19
19  20
20  21
21  22
22  23
23  24
24  25
25  26
26  27
27  28
28  29
29  30
30  31
31 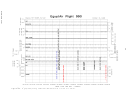 32
32  33
33  34
34  35
35 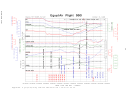 36
36 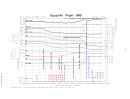 37
37 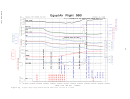 38
38  39
39  40
40  41
41  42
42  43
43  44
44  45
45  46
46  47
47  48
48  49
49  50
50  51
51  52
52  53
53  54
54  55
55  56
56  57
57  58
58  59
59  60
60  61
61  62
62  63
63  64
64  65
65  66
66  67
67  68
68  69
69  70
70  71
71  72
72  73
73  74
74  75
75  76
76  77
77  78
78  79
79  80
80  81
81  82
82  83
83  84
84  85
85  86
86  87
87  88
88  89
89  90
90  91
91  92
92  93
93  94
94  95
95  96
96  97
97  98
98  99
99  100
100  101
101  102
102  103
103  104
104  105
105  106
106  107
107  108
108  109
109  110
110  111
111  112
112  113
113  114
114  115
115  116
116  117
117  118
118  119
119  120
120  121
121  122
122  123
123  124
124  125
125  126
126  127
127  128
128  129
129  130
130  131
131  132
132  133
133  134
134  135
135  136
136  137
137  138
138  139
139  140
140  141
141  142
142  143
143  144
144  145
145  146
146  147
147  148
148  149
149  150
150  151
151  152
152  153
153  154
154  155
155  156
156  157
157  158
158  159
159  160
160 17
flight were unsuccessful; therefore, he continued the approach and landed the airplane
manually. This captain told investigators that the autopilot operated normally when he
engaged it on the ground after landing at LAX. Examination of the accident airplane’s
maintenance logbooks revealed no autopilot-related maintenance writeups, and no
subsequent autopilot anomalies were verbally reported.
th
Examination of the FDR data for the October 30
flight to LAX revealed that at
the time the captain reported he disconnected the autopilot because it was “hunting” for
the glideslope during the approach to LAX, the autopilot was operating in its LOC
(localizer approach) mode, which does not have glideslope intercept capability. The FDR
data indicated that, later in the approach to LAX, when the captain tried to reengage the
autopilot using the APP (approach) mode, which has both localizer and glideslope
intercept capability, the airplane had descended far enough below the glideslope that the
37
autopilot system could not capture the glideslope signal.
The Safety Board’s review of the FDR data revealed that nine autopilot
disconnects were recorded on the accident airplane’s 25-hour-long FDR tape: one just
before landing at Cairo the day before the accident; one just before its next landing at
EWR; four during the approach to LAX (during which the reported autopilot difficulties
occurred); one on the ground at LAX; one just before landing at JFK the night of the
accident flight; and one immediately preceding the accident sequence. No elevator
movement was recorded after the autopilot disconnect that occurred on the ground at
LAX. The elevator movements recorded following the other eight autopilot disconnects
were primarily in the trailing-edge-down (TED) direction and were less than 0.88° in
magnitude. According to Boeing, the elevator movements recorded by the accident
airplane’s FDR were consistent with the movements that would be expected as a result of
the normal operation of the autopilot on a properly rigged 767.
Accident Airplane Maintenance Information
During its investigation of the EgyptAir flight 990 accident, the Safety Board
reviewed EgyptAir’s maintenance program and maintenance recordkeeping procedures
and conducted a detailed examination of the accident airplane’s maintenance records. The
Board’s review revealed that the accident airplane had been maintained in accordance
with EgyptAir’s continuous airworthiness maintenance inspection program for its
767 fleet. Additionally, the accident airplane’s maintenance records indicated that all
applicable airworthiness directives (AD) had been complied with; no related discrepancies
were noted. Further, the Board’s review of the accident airplane’s technical log sheets
from July 29 to October 30, 1999, revealed no pertinent unresolved discrepancies.
37
According to Boeing, the autopilot is designed to capture the glideslope signal when the proper
autopilot mode is selected if the airplane is within 80 feet of the glideslope.
NTSB/AAB-02/01
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal