Doe/netl-2012/1540 Mobility And Conformance Control For Carbon Dioxide Enhanced Oil Recovery (Co2-Eor) Via Thickeners, Foams, And Gels - U.s. Department Of Energy Page 102
ADVERTISEMENT
 1
1  2
2  3
3  4
4  5
5  6
6  7
7  8
8  9
9  10
10  11
11  12
12  13
13  14
14  15
15  16
16  17
17  18
18  19
19  20
20  21
21  22
22  23
23  24
24  25
25  26
26  27
27  28
28  29
29  30
30  31
31  32
32  33
33  34
34  35
35  36
36  37
37  38
38  39
39  40
40  41
41  42
42  43
43  44
44  45
45  46
46  47
47  48
48  49
49  50
50  51
51  52
52 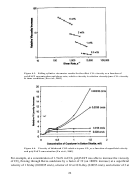 53
53  54
54  55
55  56
56  57
57  58
58  59
59  60
60  61
61  62
62  63
63  64
64  65
65  66
66  67
67  68
68  69
69  70
70  71
71  72
72 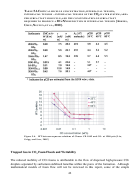 73
73  74
74  75
75  76
76  77
77  78
78  79
79  80
80  81
81  82
82  83
83  84
84  85
85  86
86  87
87  88
88 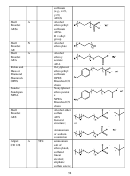 89
89 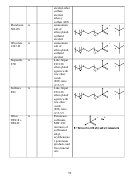 90
90  91
91  92
92  93
93  94
94  95
95  96
96  97
97  98
98  99
99  100
100  101
101  102
102  103
103 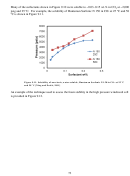 104
104  105
105  106
106  107
107 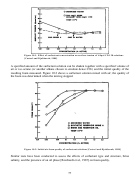 108
108  109
109  110
110  111
111 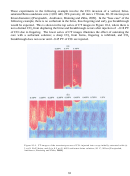 112
112  113
113 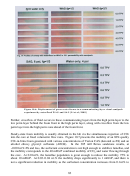 114
114  115
115  116
116  117
117 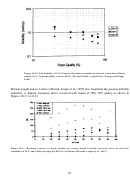 118
118  119
119  120
120  121
121  122
122  123
123  124
124  125
125  126
126  127
127  128
128  129
129 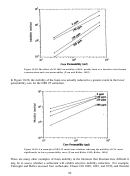 130
130  131
131  132
132  133
133  134
134  135
135  136
136  137
137 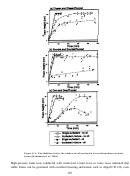 138
138  139
139  140
140  141
141  142
142  143
143  144
144  145
145 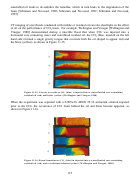 146
146 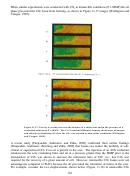 147
147  148
148  149
149  150
150  151
151  152
152  153
153  154
154  155
155 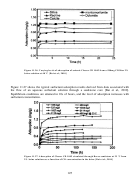 156
156  157
157  158
158 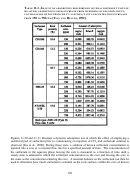 159
159  160
160  161
161  162
162  163
163  164
164  165
165 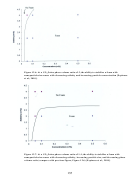 166
166  167
167  168
168  169
169  170
170  171
171  172
172  173
173  174
174  175
175  176
176  177
177  178
178  179
179  180
180  181
181  182
182  183
183  184
184  185
185  186
186  187
187  188
188  189
189  190
190  191
191  192
192  193
193  194
194  195
195  196
196  197
197  198
198  199
199  200
200  201
201  202
202  203
203  204
204  205
205  206
206  207
207  208
208  209
209  210
210  211
211  212
212  213
213  214
214  215
215  216
216  217
217  218
218  219
219  220
220  221
221  222
222  223
223  224
224  225
225  226
226  227
227  228
228  229
229  230
230  231
231  232
232  233
233  234
234  235
235  236
236  237
237  238
238  239
239  240
240  241
241  242
242  243
243  244
244  245
245  246
246  247
247  248
248  249
249  250
250  251
251  252
252  253
253  254
254  255
255  256
256  257
257  258
258  259
259  260
260  261
261  262
262  263
263  264
264  265
265  266
266  267
267 In 2008, researchers from the University of Texas at Austin and Dow Oil & Gas used a
proprietary, slightly CO
-soluble, water-soluble, nonionic surfactant dissolved at a concentration
2
of 0.1wt% in CO
at ambient temperature in a mixing vessel at 1,800 psi (~12.4 MPa)—Figure
2
9.9 [Sanders, Jones, et al., 2010]—to recover oil from a core with an effluent back-pressure
regulator set at 1,500 psi (~10 MPa) [Le et al., 2008]. The investigators assessed various modes
of surfactant injection including WAGS (water-alternating-gas with surfactant dissolved in the
CO
), SAG (surfactant-alternated-CO
with surfactant dissolved in the water) and continuous
2
2
CO
-dissolved-surfactant injection (no alternate injection of water used) and found that the
2
injection of the CO
-surfactant solution into the waterflooded core without the use of alternating
2
water slugs yielded higher oil recovery than the other injection modes.
o
Figure 9.9. Solubility of a typical Dow CO
soluble surfactant in CO
at 60
C [Sanders, Jones,
2
2
et al., 2010]
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and NETL are also actively attempting to identify
commercially available, CO
soluble, water soluble, nonionic surfactants that are capable of
2
dissolving in CO
at conditions commensurate with CO
EOR at a concentration great enough to
2
2
stabilize a foam. Foams were then generated in a windowed vessel by mixing CO
, brine, and an
2
amount of surfactant corresponding to that which could dissolve in the CO
at test conditions.
2
Foams were also generated in situ in a mobility apparatus in which a high-pressure CO
2
surfactant solution was injected into a brine saturated core. Some of the surfactants selected for
this study are illustrated in Figure 9.10. There are two general classes of surfactants considered
in this study: those with a phenol group (benzene ring) in the middle of the surfactant and those
without the phenol group. In the foam stability tests, the alkylphenol ethoxylates were capable
of stabilizing the CO
-in-5% NaCl brine emulsions more effectively than the surfactants lacking
2
the aromatic ring, but the surfactants without the aromatic group may be advantageous in that
71
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal









