Doe/netl-2012/1540 Mobility And Conformance Control For Carbon Dioxide Enhanced Oil Recovery (Co2-Eor) Via Thickeners, Foams, And Gels - U.s. Department Of Energy Page 171
ADVERTISEMENT
 1
1  2
2  3
3  4
4  5
5  6
6  7
7  8
8  9
9  10
10  11
11  12
12  13
13  14
14  15
15  16
16  17
17  18
18  19
19  20
20  21
21  22
22  23
23  24
24  25
25  26
26  27
27  28
28  29
29  30
30  31
31  32
32  33
33  34
34  35
35  36
36  37
37  38
38  39
39  40
40  41
41  42
42  43
43  44
44  45
45  46
46  47
47  48
48  49
49  50
50  51
51  52
52 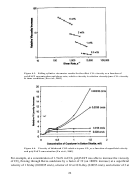 53
53  54
54  55
55  56
56  57
57  58
58  59
59  60
60  61
61  62
62  63
63  64
64  65
65  66
66  67
67  68
68  69
69  70
70  71
71  72
72 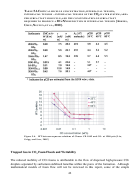 73
73  74
74 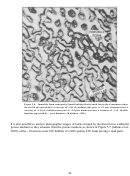 75
75  76
76  77
77  78
78  79
79  80
80  81
81  82
82  83
83  84
84  85
85  86
86  87
87  88
88 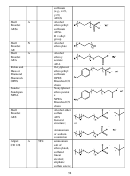 89
89 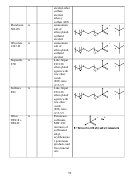 90
90  91
91  92
92  93
93  94
94  95
95  96
96  97
97  98
98  99
99  100
100  101
101  102
102 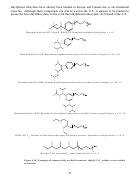 103
103 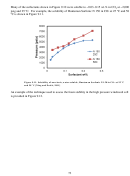 104
104  105
105  106
106  107
107 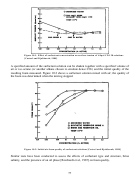 108
108  109
109  110
110  111
111  112
112  113
113  114
114  115
115  116
116  117
117  118
118  119
119  120
120  121
121  122
122  123
123  124
124  125
125  126
126  127
127  128
128  129
129  130
130  131
131  132
132  133
133  134
134  135
135  136
136  137
137 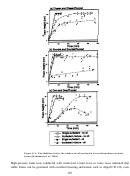 138
138  139
139  140
140  141
141  142
142  143
143  144
144  145
145 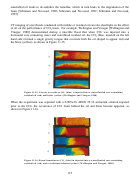 146
146 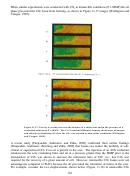 147
147  148
148  149
149  150
150  151
151  152
152  153
153  154
154  155
155 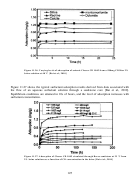 156
156  157
157  158
158 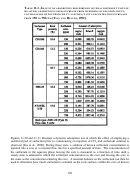 159
159  160
160  161
161  162
162  163
163  164
164  165
165 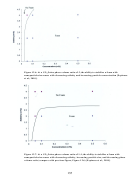 166
166  167
167  168
168  169
169  170
170  171
171  172
172  173
173  174
174  175
175  176
176  177
177  178
178  179
179  180
180  181
181  182
182  183
183  184
184  185
185  186
186  187
187  188
188  189
189  190
190  191
191  192
192  193
193  194
194  195
195  196
196  197
197  198
198  199
199  200
200  201
201  202
202  203
203  204
204  205
205  206
206  207
207  208
208  209
209  210
210  211
211  212
212  213
213  214
214  215
215  216
216  217
217  218
218  219
219  220
220  221
221  222
222  223
223  224
224  225
225  226
226  227
227 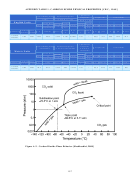 228
228  229
229  230
230  231
231 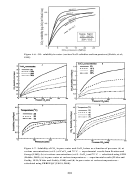 232
232  233
233  234
234  235
235  236
236  237
237  238
238  239
239  240
240  241
241  242
242  243
243  244
244  245
245  246
246  247
247  248
248  249
249  250
250  251
251  252
252  253
253  254
254  255
255  256
256  257
257  258
258  259
259  260
260  261
261  262
262  263
263  264
264  265
265  266
266  267
267 flood, while the remaining pressure increase was attributed to the foam. The Hall plot result
indicated that the polymer foam had a resistance factor about twice as large as the polymer +
surfactant pre-slug. Further, tracer monitoring and injection profile results indicated that the pre-
treatment range of velocities in the various layers became more uniform and the proportion of
fluids entering the least permeable zones increased notably (e.g., 16%–23% in the top 0.5 m of
the C26-G9 well) indicating the increased resistance of the foam and a more uniform injection
profile amongst the layers. The most promising results were related to the cumulative oil
production in the 12 production wells. Before the pilot, the combined oil and production rate
was 566 tons/day, only 23 tons/day of which were oil, and the water cut was 97.2%. Halfway
through the pilot, the combined oil and production rate was 704 tons/day, the oil production rate
was 36 tons/day, and the water cut was 94.9%.
PetroChina Daqing Oilfield Co.’s Sabei Field, Xing 7-1-33 and Bei 2-Ding 2-59 Well
Clusters; SAG Polymer Foam; Conformance Control [He et al., 2010].
The Daqing oilfield is a multi-layer, heterogeneous sandstone system in an inland basin. The
o
reservoir temperature of this 1,000 m deep formation is 45
C. Oil viscosity at reservoir
conditions range between 6 to 9 cP. The permeability of the sands reaches values as high as
1000 mD, and the Dykstra Parsons coefficient of permeability variation ranges from 0.4 to 0.7
[Dong et al., 2008]. During the late 1980s, a polymer flooding pilot was conducted at Daqing,
which ultimately led to the initiation of the world’s largest polymer flood in 1996. By the end of
2007, the polymer flood resulted in the production of more than 10 million tons (73 MM bbl.) of
oil per year for six consecutive years.
The main pay zone in Daqing has now been flooded for more than thirty years and is exhibiting
water-cut values greater than 90%. Reservoir studies indicated that foam flooding could be a
viable means of recovering the remaining oil in the main pay zone via improved sweep
efficiency, while recovery of oil from the less permeable zones could be accomplished via
conformance and mobility control. The Sabei field in Daqing was selected for a field pilot of
polymer-stabilized nitrogen foam flooding because of its particularly high water cut of ~96%
associated with the presence of very high permeability watered-out zones. A well cluster, Bei 2
Ding 2-59, in the eastern portion of Area Bei-3 of the Sabei field was selected for the pilot test to
assess conformance control and oil production response.
It was anticipated that a relatively small, near-wellbore nitrogen foam treatment would
effectively divert the subsequently injected nitrogen away from the thief zone, improve the
injection profile, increase oil production, and decrease water production [He, et al., 2010]. The
aqueous foaming solutions studied for this field contained 0.3–0.5wt% surfactant and 30–1,500
ppm of a polymeric stabilizer.
The Bei 2 Ding 2-59 polymer-stabilized nitrogen foam pilot was conducted from October 2005
to January 2006. The cluster is composed of two central production wells, three injection wells,
and seven corner production wells in the peripheral zone. The targeted sandstone formations, Pu
II and Gao I, are 900–1,200 m deep in these clusters with permeability values ranging from 140
–900 mD. The foam was injected into one well at a time, with a maximum injection period of
3
one month per well. The cumulative injection into the three injectors was 4,477 m
of the
140
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal









