Instructional Manual For Clarification Of Startup In Source Categories Affected By New Source Performance Standards - U.s. Environmental Protection Agency - 1979 Page 104
ADVERTISEMENT
 1
1  2
2  3
3  4
4  5
5  6
6  7
7  8
8  9
9  10
10  11
11  12
12  13
13  14
14  15
15  16
16  17
17  18
18 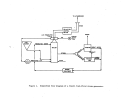 19
19  20
20  21
21  22
22 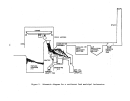 23
23  24
24  25
25  26
26  27
27  28
28  29
29  30
30  31
31  32
32 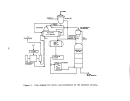 33
33  34
34  35
35  36
36  37
37  38
38  39
39  40
40  41
41  42
42 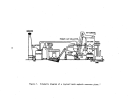 43
43  44
44  45
45  46
46  47
47 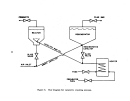 48
48  49
49  50
50 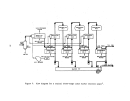 51
51  52
52  53
53  54
54  55
55  56
56  57
57  58
58  59
59  60
60 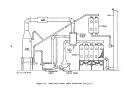 61
61  62
62  63
63  64
64  65
65 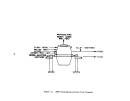 66
66  67
67  68
68  69
69  70
70 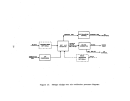 71
71  72
72  73
73  74
74  75
75  76
76  77
77  78
78  79
79  80
80  81
81  82
82  83
83  84
84  85
85  86
86  87
87  88
88  89
89  90
90  91
91  92
92  93
93  94
94  95
95  96
96  97
97 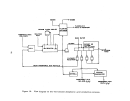 98
98  99
99  100
100  101
101 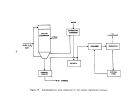 102
102 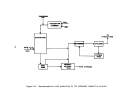 103
103  104
104  105
105  106
106 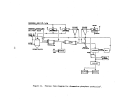 107
107  108
108  109
109  110
110 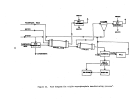 111
111  112
112  113
113  114
114 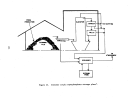 115
115  116
116  117
117  118
118  119
119  120
120  121
121 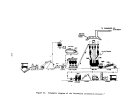 122
122  123
123  124
124  125
125  126
126  127
127  128
128  129
129  130
130 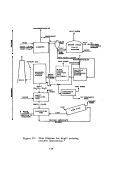 131
131  132
132  133
133  134
134  135
135  136
136  137
137 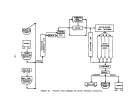 138
138  139
139  140
140  141
141 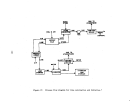 142
142  143
143  144
144  145
145  146
146 perform their own debugging procedures when the equipment is delivered.
The
plant would check the circulation pump for alignment, rotation, and with
couplings disengaged, and also check bearings and packing.
All acid-handling
equipment is filled with fresh water for about 2 hours during which time leaks
are detected and pumps, ammeters, flow meters, etc. are checked for capacity
and calibration.
A plant engineer will also inspect the equipment for proper
welds and to verify the construction material (usually Hastelloy G - 20 to 30
percent nickel).
Operating vacuum is then pulled on the system and held for
at least 8 hours to check for vacuum leaks.
Steam lines are then blown out
to remove mill scale, welding rods, or other extraneous materials.
Water and
steam are then introduced to the plant and the water is evaporated for 5 to 6
hours to check pumps, instrument loops, control valves, and other pertinent
components.
Startup Operations
Upon completion of the process equipment checks, the system is recharged
with acid and the acid feed is
ini~iated;
this can be considered as plant
startup.
For normal circumstances involving no equipment failures or innovative
designs requiring additional process evaluations, the preliminary equipment
checks consume about 2 weeks and the maximum design rate can be achieved in
about 48 hours.
Approximately 2 to 3 weeks after the startup period, a per-
formance run of about 3 days will begin, during which time all phases of opera-
tionrnust be as specified including emission rates and plant efficiency ex-
pressed as unit weight of product per unit weight of steam input.
Under normal
conditions, 180 days is adequate time for conductance of source tests·,
92
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal