Instructional Manual For Clarification Of Startup In Source Categories Affected By New Source Performance Standards - U.s. Environmental Protection Agency - 1979 Page 132
ADVERTISEMENT
 1
1  2
2  3
3  4
4  5
5  6
6  7
7  8
8  9
9  10
10  11
11  12
12  13
13  14
14  15
15  16
16  17
17  18
18 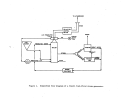 19
19  20
20  21
21  22
22 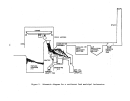 23
23  24
24  25
25  26
26  27
27  28
28  29
29  30
30  31
31  32
32 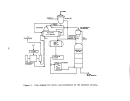 33
33  34
34  35
35  36
36  37
37  38
38  39
39  40
40  41
41  42
42 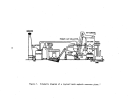 43
43  44
44  45
45  46
46  47
47 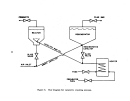 48
48  49
49  50
50 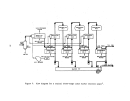 51
51  52
52  53
53  54
54  55
55  56
56  57
57  58
58  59
59  60
60 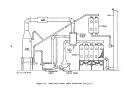 61
61  62
62  63
63  64
64  65
65 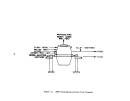 66
66  67
67  68
68  69
69  70
70 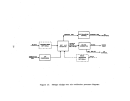 71
71  72
72  73
73  74
74  75
75 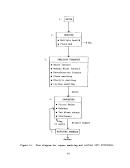 76
76  77
77  78
78  79
79  80
80  81
81  82
82  83
83  84
84  85
85  86
86  87
87  88
88  89
89  90
90  91
91  92
92  93
93 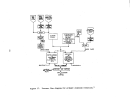 94
94  95
95  96
96  97
97 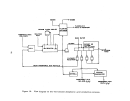 98
98  99
99  100
100  101
101 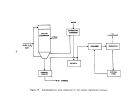 102
102 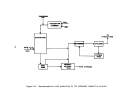 103
103  104
104  105
105  106
106  107
107  108
108  109
109  110
110 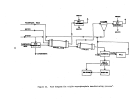 111
111  112
112  113
113  114
114 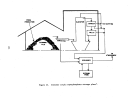 115
115  116
116  117
117  118
118  119
119  120
120  121
121  122
122  123
123  124
124  125
125  126
126  127
127  128
128  129
129  130
130 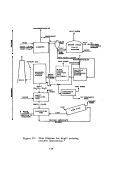 131
131  132
132  133
133  134
134  135
135  136
136  137
137 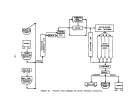 138
138  139
139  140
140  141
141 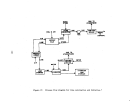 142
142  143
143  144
144  145
145  146
146 The pre-"startup operations of a kraft pulp mill lime kiln are similar to
those of a rotary kiln used in the manufacture of lime.
Once the kiln has been
erected and before it is bolted down, various tests are conducted to check its
alignment and rotation.
Once the kiln passes these preliminary tests, it is
secured and rechecked for alignment and rotation.
A third examination is made
when heat is first introduced to the kiln.
The most important pre-startup operation of the kiln is the seasoning or
drying out of the brick refractory lining.
New refractory usually contains
residual amounts of water which must be driven out before the lime slurry can
be fed into the kiln.
The drying out process is slow, requiring a gradual
warming of the bricks to prevent cracking or loosening.
The kiln seasoning
process normally takes 3 to 5 days.
Once the refractory has been properly seasoned and the burners and fuel
supply lines have been checked out, the kiln is ready to receive the lime slurry.
Lime kilns operated at kraft pulp mills are usually fired with gas or oil.
High energy venturi scrubbers are normally used to control kiln emissions.
Startup Operations
The performance of a facility affected by this subpart is dependent upon
process operations upstream and downstream of the particular unit.
Six major
operations within
8.
kraft pulp mill are the:
power boilers, digester system,
recovery furnaces, lime kiln, bleach plant, and paper machines.
The startup
of a mill requires the operation of at least the first four of these processes.
Some mills will not operate bleach facilities nor paper machines.
The power
boilers, not affected under this subpart, are the first operations to be brought
on line.
Startup of the facilities affected under this subpart is considered to be
when wood chips and white liquor are first fed to the digesters with the intent
to produce pulp.
Mill operators contacted stated that it may t.ake from twelve
to twenty-four hours from the time the first cook is initiated until recongniz-
able pulp comes out of the thickeners.
The first pulp produced is not of·any
commercial or production value.
Due to the large capital outlay and high daily·
operating costs, this situation will not last long and mill operators will con-
centrate their efforts on fine tuning process equipment in order to produce
useable pulp as soon as possible.
Once the first cook has been initiated, it will take a day or two before
enough black liquor is produced to fire in the recovery furnace.
Likewise, it
will be one to two days after black liquor is first burned b"efore enough lime
slurry is generated from the causticizing tank to be fed into the lime kiln.
Because white liquor will not be generated from process operations until two
to four days after commencement of the initial cook, the white liquor and
caustic (lime) must be purchase9 or obtained from some other source in order
to start the pulping process.
Once the chemical recovery cycle has been com-
pleted, it becomes almost entirely se1f-sustaining.
In summary, it normally
takes from two to four days after initial startup;
i.e~,
the introduction of
wh Lte liquor and wood chips into the d:f.gester, before all the affected facili-
ties of a kraft pulp mill become operat:1.onal.
120
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal