Instructional Manual For Clarification Of Startup In Source Categories Affected By New Source Performance Standards - U.s. Environmental Protection Agency - 1979 Page 108
ADVERTISEMENT
 1
1  2
2  3
3  4
4  5
5  6
6  7
7  8
8  9
9  10
10  11
11  12
12  13
13  14
14  15
15  16
16  17
17  18
18 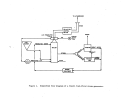 19
19  20
20  21
21  22
22 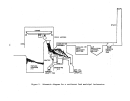 23
23  24
24  25
25  26
26  27
27  28
28  29
29  30
30  31
31  32
32 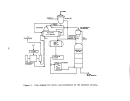 33
33  34
34  35
35  36
36  37
37  38
38  39
39  40
40  41
41  42
42 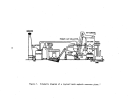 43
43  44
44  45
45  46
46  47
47 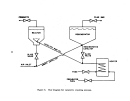 48
48  49
49  50
50 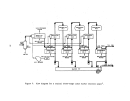 51
51  52
52  53
53  54
54  55
55  56
56  57
57  58
58  59
59  60
60 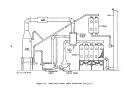 61
61  62
62  63
63  64
64  65
65 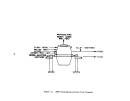 66
66  67
67  68
68  69
69  70
70 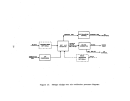 71
71  72
72  73
73  74
74  75
75 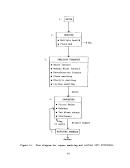 76
76  77
77  78
78  79
79  80
80  81
81  82
82  83
83  84
84  85
85  86
86  87
87  88
88  89
89  90
90  91
91  92
92  93
93 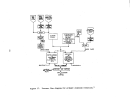 94
94  95
95  96
96  97
97 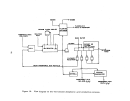 98
98  99
99  100
100  101
101 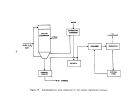 102
102 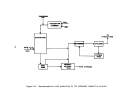 103
103  104
104  105
105  106
106  107
107  108
108  109
109  110
110 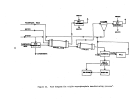 111
111  112
112  113
113  114
114 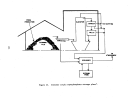 115
115  116
116  117
117  118
118  119
119  120
120  121
121 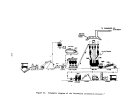 122
122  123
123  124
124  125
125  126
126  127
127  128
128  129
129  130
130 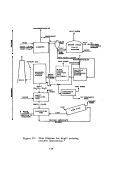 131
131  132
132  133
133  134
134  135
135  136
136  137
137 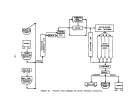 138
138  139
139  140
140  141
141 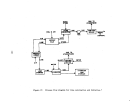 142
142  143
143  144
144  145
145  146
146 1 percent.
Dry product is then cooled by a countercurrent flow of air in a
rotary cooler and screened with coarse material being returned to the ammoniator.
In some plants ,. hot screening is employed such that cooling is achieved prior
to storage and shipping.
Exhaust gases from the dryer (and cooler) pass through
cyclones or wet scrubbers for particulate removal while effluent from the ammo-
niator are usually scrubbed with incoming phosphoric acid prior to discharge
to the atmosphere.
Pre-Startup Operations.
As
depicted in Figure 21, the process consists of a wet end (prior to
ammoniator) and a dry end (ammoniator and downstream).
All equipment on the
wet end is water-batched to check for leaks and proper valve operation.
All
pumps, electrical connections, and instrumentation are thoroughly cheeked and
evaluated with respect to proper operation and calibration.
The granulator, dryer, and cooler (if used) are all inclined slightly and
must be mechanically checked for proper rotation and tracking.
The gear box
and driving mechanism must mesh properly and operate without excess noise or
heat.
This can take from 2 hours to 2 weeks.
The dryer furnace would undergo preliminary operations similar to those
described previously for fossil fuel boilers.
Once all equipment is installed and verified for proper installation, con-
nections and mechanical operation, the plant is operated dry with recycle ma-
terial (rather than slurry) to check conveyors (recycle, belt, and elevator)
for binding prior to initial charging.
All other equipment is also run dry
prior to initial charging.
Startup Operations
Once all process equipment has been operated with dry recycle material and
has been shown to operate reliably, the preneutralizer (or reactor) is charged
with ammonia. water, and phosphoric acid and the process is begun.
Initial
charging varies depending on the size of the plant but usually would require
45-91 metric tons (50-100 tons) of DAP.
The key, controlling factor with respect to proper operation of the entire
plant is the particle size of the finished material.
Fines are recycled to the
granulator while oversize material is recycled to the mills and back. to the
granulator.
Recycling is important to the process and too much on-size material
can also be a problem.
Normal recycle to product ratio is 3:1.
Throughout the
life of the plant, the operators are constantly trying to find the one limiting
piece of equipment which could affect the entire facility's capability.
Startup is best defined as the time of initial firing of the furnace and
charging of the preneutralizer with ammonia and phosphoric acid.
This would
be the Brat time for potential fluoride emissions and would come after all
equIpment has been thoroughly debugged.
The controlling factor would be the
specifIc gravity of the slurry.
It would normally take about 2 to 6 hours to
sufficiently heat and charge the system and full production rate could be
achieved In 2 weeks.
A plant acceptance run would usually be performed shortly
thereafter.
96
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal