Instructional Manual For Clarification Of Startup In Source Categories Affected By New Source Performance Standards - U.s. Environmental Protection Agency - 1979 Page 39
ADVERTISEMENT
 1
1  2
2  3
3  4
4  5
5  6
6  7
7  8
8  9
9  10
10  11
11  12
12  13
13  14
14  15
15  16
16  17
17  18
18 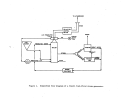 19
19  20
20  21
21  22
22 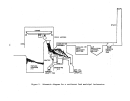 23
23  24
24  25
25  26
26  27
27  28
28  29
29  30
30  31
31  32
32 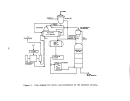 33
33  34
34  35
35  36
36  37
37  38
38  39
39  40
40  41
41  42
42 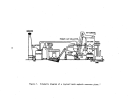 43
43  44
44  45
45  46
46  47
47 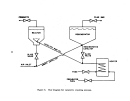 48
48  49
49  50
50 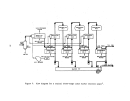 51
51  52
52  53
53  54
54  55
55  56
56  57
57  58
58  59
59  60
60 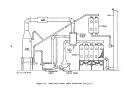 61
61  62
62  63
63  64
64  65
65 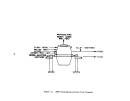 66
66  67
67  68
68  69
69  70
70 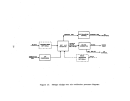 71
71  72
72  73
73  74
74  75
75 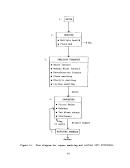 76
76  77
77  78
78  79
79  80
80  81
81  82
82  83
83  84
84  85
85  86
86  87
87  88
88  89
89  90
90  91
91  92
92  93
93 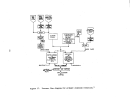 94
94  95
95  96
96  97
97 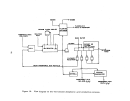 98
98  99
99  100
100  101
101 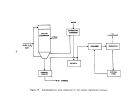 102
102 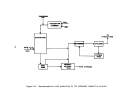 103
103  104
104  105
105  106
106 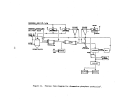 107
107  108
108  109
109  110
110 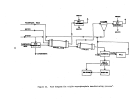 111
111  112
112  113
113  114
114 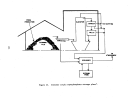 115
115  116
116  117
117  118
118  119
119  120
120  121
121 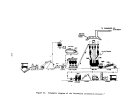 122
122  123
123  124
124  125
125  126
126  127
127  128
128  129
129  130
130 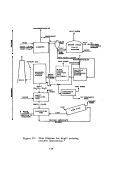 131
131  132
132  133
133  134
134  135
135  136
136  137
137 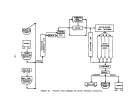 138
138  139
139  140
140  141
141 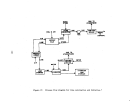 142
142  143
143  144
144  145
145  146
146 demonstrated technology for control of 802 emissions is the dual absorption
process and for acid mist is the high efficiency mist eliminator.
An
alternate
control system consists ofa hydrogen peroxide scrubb:(.ng system (DuPont's
"Tysul" system).
Pre-Startup Operations
Once equipment is delivered to the p,l,ant, certain mechanical checks can
be performed prior to final
~ooktips
. . Gas and steam piping systems undergo
rigorous pressure testing at,
l~
't'imes their design operating pressure.
The
waste heat boiler undergoes.hy,qrostatic testing according to ASME codes for
fossil fuel-fired pressure
vessel~
•. ' All other acid .and water piping are tested
(primarily for leaks) at their normal operating pressure.
Pumps are rotated to
e~sure ptop~r
operation and blowers may be run for a
day or two to check for ba,lan'ce and'v!bratioIL
Lubrication systems would also
,
, . J !
'
be analyzed.
i
During the final stageso~. construc;tion, major vessels such as gas to gas
heat exchangers, absorbers, "!cOnverter, and sulfur storage tanks are manually
inspected by an experienced "start\lp engineer prior to "closing."
Following
this inspection procedure,the plant would be ready to begin the initial
heating of the catalyst.
Preparation for catalyst bed heating begins with the initial low level
firing of the combustion chambe:r', (sulfur burner).
The combustion chamber con-
sists of multiple layers of brickwork which must be heated slowly to about
S7l
o
e
(l.600
0
F) to eliminate any entrained moisture.
This procedure can take
from 7 to 12 days.
The waste heat boiler will then undergo a boilout procedure wherein the
unit is filled with water and degreasing chemicals, warmed, flushed, and
drained
t
and then ilas all gaskets replaced and is refilled with normal boiler
water.
Concurrently
t
the d
l;ylng
and' absorbing towers are water-batched for
leak detection followed by"'(1Cttd recirculation.
Startup Operations , •. ' , "
Prior to the initia:l:"f'eed: .. of raw material,' the heating 'of the system is
accomplished in th:r~.e phase's' totaling about 30 hr. ,Phase I consists of an
l8-hr period to
pr~~~at
the furnace; Phase
I I
takes about 2 hr to blow pre-
heated air through
:~he
converter'; and Phase III requires 10 hr to reheat
the furnace and tl\en heat. the catalyst bed to the ignition temperature.
Startup follows the preheating period and is best defined as the first
time raw material is fe'd~'to the system, whether it be sulfur or spent acid
(alkylation chemical.. nitration sludge and hydrogen sulfide).
The raw material
feed is begun at
abotif~25
percellt of the designral;:e and is gradually brought
up to full load depending on
th~proper
functioning of a.U other plant com ....
ponents.
If
there
ar~',no
difficulties, full pr'Oduction rate can be achieved
in 24 to 72 hr.
The most common problem which results in plant shutdown
is gas leakage in some part of the system and this will usually occur in
1/3
of new plant startups.
27
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal