Instructional Manual For Clarification Of Startup In Source Categories Affected By New Source Performance Standards - U.s. Environmental Protection Agency - 1979 Page 97
ADVERTISEMENT
 1
1  2
2  3
3  4
4  5
5  6
6  7
7  8
8  9
9  10
10  11
11  12
12  13
13  14
14  15
15  16
16  17
17  18
18 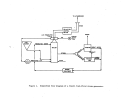 19
19  20
20  21
21  22
22 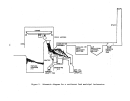 23
23  24
24  25
25  26
26  27
27  28
28  29
29  30
30  31
31  32
32 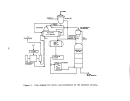 33
33  34
34  35
35  36
36  37
37  38
38  39
39  40
40  41
41  42
42 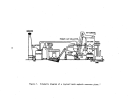 43
43  44
44  45
45  46
46  47
47  48
48  49
49  50
50  51
51  52
52  53
53  54
54  55
55  56
56  57
57  58
58  59
59  60
60  61
61  62
62  63
63  64
64  65
65 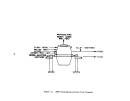 66
66  67
67  68
68  69
69  70
70 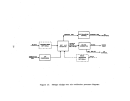 71
71  72
72  73
73  74
74  75
75  76
76  77
77  78
78  79
79  80
80  81
81  82
82  83
83  84
84  85
85  86
86  87
87  88
88  89
89  90
90  91
91  92
92  93
93  94
94  95
95  96
96  97
97 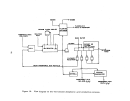 98
98  99
99  100
100  101
101  102
102  103
103  104
104  105
105  106
106  107
107  108
108  109
109  110
110 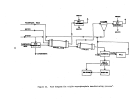 111
111  112
112  113
113  114
114 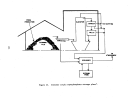 115
115  116
116  117
117  118
118  119
119  120
120  121
121 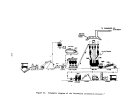 122
122  123
123  124
124  125
125  126
126  127
127  128
128  129
129  130
130 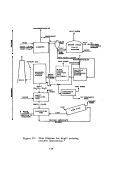 131
131  132
132  133
133  134
134  135
135  136
136  137
137 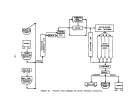 138
138  139
139  140
140  141
141 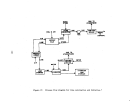 142
142  143
143  144
144  145
145  146
146 WET PROCESS - PHOSPHORIC ACID PLANTS - SUBPART T
§60.200 - 60.204
Introduction
For the purposes of this regulation, wet process phosphoric acid plants
are defined as any facilities manufacturing phosphoric acid by reacting phos-
phate rock and acid.
Affected facilities include any combination of reactors,
filters, evaporators, and hotwells.
Emissions of total fluorides are limited
to 10 g/metric ton (0.02 lb/ton) of equivalent P20S feed.
Equivalent P2 0 S
feed is defined as the quantity of phosphorous, expressed as phosphorous
pentoxide, fed to the process.
Sources constructed, reconstructed, or modi-
fied after October 22, 1974, are subject to the regulation.
Process Description
The sulfuric acid or wet process produces phosphoric acid by the reaction
of phosphate rock with sulfuric acid which also results in the precipitation of
calcium sulfate (gypsum).
Figure 18 is a simplified flow diagram of the pro-
cess.
Phosphate rock is ground in a special ball mill with dilute phosphoric
acid (recycled) and the resultant slurry mixture is then passed into multiple
reactor and digesting tanks for reaction with sulfuric acid.
Cooling is re-
quired to remove the heat of reaction.
Water vapor and gaseous impurities are
carried to an absorber where fluosilicic acid is recovered.
Acid digestion of
the slurry requires 4 to
8
hours at temperatures of about 750C (167 0 F).
Violent
agitation and close temperature control are required for the production of
uniform, easily washed and filtered gypsum (CaS04 • 2H20) crystals.
Without
this close control, the anhydrite would form, become subsequently hydrated, and
result in plugging of pipes.
Slurry from the digester tanks passes into horizontal, rotating, tilting-
pan-type vacuum filters where phosphoric acid (30 to 35 percent P20S) is removed
from the filter cake.
This acid filtrate is then concentrated to 54 percent
P20S by evaporation.
Pre-Startup Operations
Mechanical checkout is begun as soon as specific units or groups of inter-
related units are reported as mechanically complete by the construction con-
tractor.
These checks include:
•
alignment of all motor driven equipment
•
hydrostatic testing of all liquid handling equipment
85
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal