Instructional Manual For Clarification Of Startup In Source Categories Affected By New Source Performance Standards - U.s. Environmental Protection Agency - 1979 Page 106
ADVERTISEMENT
 1
1  2
2  3
3  4
4  5
5  6
6  7
7  8
8  9
9  10
10  11
11  12
12  13
13  14
14  15
15  16
16  17
17  18
18 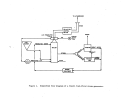 19
19  20
20  21
21  22
22 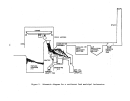 23
23  24
24  25
25  26
26  27
27  28
28  29
29  30
30  31
31  32
32 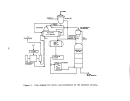 33
33  34
34  35
35  36
36  37
37  38
38  39
39  40
40  41
41  42
42 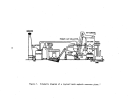 43
43  44
44  45
45  46
46  47
47  48
48  49
49  50
50  51
51  52
52  53
53  54
54  55
55  56
56  57
57  58
58  59
59  60
60  61
61  62
62  63
63  64
64  65
65 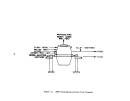 66
66  67
67  68
68  69
69  70
70  71
71  72
72  73
73  74
74  75
75  76
76  77
77  78
78  79
79  80
80  81
81  82
82  83
83  84
84  85
85  86
86  87
87  88
88  89
89  90
90  91
91  92
92  93
93  94
94  95
95  96
96  97
97 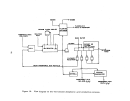 98
98  99
99  100
100  101
101 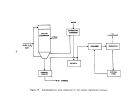 102
102 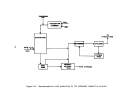 103
103  104
104  105
105  106
106  107
107  108
108  109
109  110
110 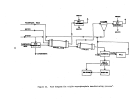 111
111  112
112  113
113  114
114  115
115  116
116  117
117  118
118  119
119  120
120  121
121  122
122  123
123  124
124  125
125  126
126  127
127  128
128  129
129  130
130  131
131  132
132  133
133  134
134  135
135  136
136  137
137 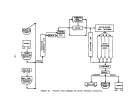 138
138  139
139  140
140  141
141  142
142  143
143  144
144  145
145  146
146 Introduction'
DIAMMONIUM PHOSPHATE PLANTS - SUBPART V
§60.220 - 60.224
Granular diammonium phosphate plants regulated in this part are defined
as any plant manufacturing granular diarnmonium phosphate by reacting phosphoric
acid with ammonia.
Affected facilities within each plant include any combina-
tion of reactors, granulators, dryers, coolers, screens, and mills.
Emissions
of total fluorides are limited to 30 g/rnetric ton (0.06 lb/ton) of equivalent
P20S feed (the quantity of phosphorous, expressed as phosphorous pentoxide,
fed to the process).
Sources constructed, reconstructed or modified after
October 22, 1974, are subject to the regulation.
Process Description
Two possible methods exist for the manufacture of diammonium phosphate
(DAP); one results in run-of-pile product (large pellets), made in a TVA cone
mixer, which cures in a storage pile and is then granulated; the other results
in a slurry which is granulated in an ammoniator or granulator.
Since the
latter (slurry) process is the most likely to be employed in new facilities,
the following process description, flow diagram, and startup operations will
apply to this type.
The production of DAP (high-analysis fertilizer) results in different
compositions depending on the type of phosphoric acid used in the process.
If
phosphoric acid made by burning elemental phosphorous in an electric furnace is
used, the resulting fertilizer composition is 21-54-0 (21 percent total nitrogen,
54 percent available phosphate as phosphorous pentoxide, and 0 percent soluble
potash as K20).
If wet-process phosphoric acid is used, the resulting analysis
is
l8~46-0.
A flow diagram of a typical plant is illustrated in Figure 21.
Vapor or liquid anhydrous ammonia and phosphoric acid are proportioned to
an agitated atmospheric tank (preneutralizer) to maint.:lin a ratio of 1.3:1.5
moles of ammonia per mole of phosphoric acid.
The exothermic reaction that
takes place results in the evaporation of approximately one tenth of the
product as water.
The slurry obtained from the preneutralizer flows into the
amrnoniator-granulator at about 121°C (250
0
F).
As it is distributed over the
bed of solid material, it reacts with additional ammonia fed through a distribu-
tor pipe beneath the bed to complete the reaction to a mole ratio of 2.0 (diam-
monium phosphate).
Material from finished product screening is recycled to
the ammoniator along with additional solid raw materials to aid in moisture
control.
The moist granules exiting the arnrnoniator proceed through an oil-
or gas-fired concurrent rotary dryer where moisture content is lowered to about
94
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal