Review Of Organic Chemistry Page 14
ADVERTISEMENT
Organic Chemistry I Review: Highlights of Key Reactions, Mechanisms, and Principles
14
Summary of Mechanisms, Ch. 7 + 8.
Alkene Synthesis and Reactions.
1
HBr
Br
(no peroxides)
Note: For unsymmetrical alkenes,
H Br
Br
Br
protonation occurs at the less
substituted alkene carbon so that
H
H
H
Cation
Protonate
the more stable cation forms
H
Capture
H
(3º > 2º > 1º), in keeping with the
product stability-reactivity principle
+ Br
CH
CH
3
3
vs.
H
H
H
H
3º
2º
2
CH
3
HBr
H
peroxides
Br
both cis and trans
Note 2: Hydrogenation of
Br
H Br
H
the radical comes from either
+
Br
Br
H
Br
face, thus cis/trans
Brominate
Hydrogen
H
mixture results
H
Transfer
CH
3
H
top
Note 1: For unsymmetrical alkenes,
Br
bromination occurs at the less
CH
CH
H
3
3
cis
substituted alkene carbon so that
vs.
Br
bottom
the more stable radical forms
H
Br
Br
(3º > 2º > 1º), in keeping with the
CH
H
H
3
H
3º
product stability-reactivity principle
2º
Br
H
trans
3
CH
3
+
H
O, H
OH
2
H
H
OH
O
2
OH
H -H
H
H
H
Cation
H
Protonate
Deprotonate
H
H
Capture
H
Note: For unsymmetrical alkenes, protonation again occurs at the less substituted end of the
alkene, in order to produce the more stable radical intermediate (3º > 2º > 1º)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10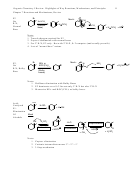 11
11 12
12 13
13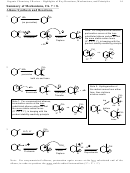 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20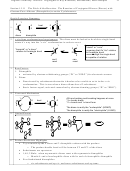 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30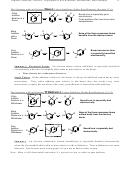 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34