Review Of Organic Chemistry Page 25
ADVERTISEMENT
Organic Chemistry I Review: Highlights of Key Reactions, Mechanisms, and Principles
25
16.5,6, 7 Aromatic, Antiaromatic, Nonaromatic. Huckel’s Rule: For a planar, continuous ring of
2
p-orbitals, (sp
all around):
• If the number of π-electrons = 2,6,10 etc. (4N + 2) AROMATIC, STABILIZED
• If the number of π-electrons = 4,8,12 etc. (4N ) Anti-aromatic, destabilized
• Why: the 4N+2 rule always goes with favorable Frost diagrams: bonding and only bonding
MO’s are always filled.
• Generality: Huckel’s Rule applies for cycles, bicycles, ionic compounds, and heterocycles.
a. Cycles (one-ring)
b. Polycycles (2 or more)
c. Ionic rings
d. Heterocycles
Keys to Recognizing Aromatic or Not:
2
1. Do you have an uninterrupted sp
ring?
2. Apply Huckel’s Rule: Do you have 2,6,10 etc. π electrons?
3. Applying Huckel’s Rule requires that you can accurately count your π-electrons. Be able to
count:
• Anions: contribute 2 π-electrons
• Cations: contribute 0 π-electrons
• Heteroatoms (O or N): can provide 2 π-electrons if it helps result in aromatic stability.
16.8 Aromatic Ions
3 common, important Aromatic Ions
15.2 Heterocyclic Aromatics. Memorize 3.
N H
O
N
Pyridine
Pyrrole
Furan
N
H
O
N
Nitrogens: Atom hybridization, Lone-Pair hybridization, and Basicity
• Amine nitrogens are normally basic, but not when the N-lone pair is p-hybridized
• Rule: If a nitrogen lone pair is p (used in conjugation) nonbasic
3
2
• Nitrogen lone-pair basicity: sp
> sp
>>> p
Situations
N-Atom
N-Lone Pair
N-Basicity
3
3
1. Isolated
sp
sp
Normal
2
2
2. Double Bonded
sp
sp
Normal
(a
little
below,
but
not
much)
2
3. Conjugated (not itself double bonded,
sp
p
Nonbasic
but next to a double bond)
p-lone pairs are less basic because conjugation stability in the reactant is lost upon protonation.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10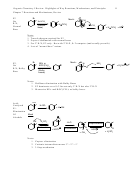 11
11 12
12 13
13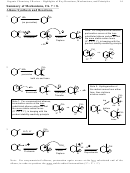 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20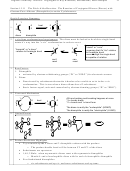 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30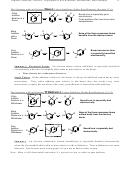 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34