Review Of Organic Chemistry Page 27
ADVERTISEMENT
Organic Chemistry I Review: Highlights of Key Reactions, Mechanisms, and Principles
27
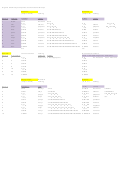
5 Major Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions
Ortho/Para
Activating/
Or Meta
Deactivating
Directing
Book
Br
H
Deactivating
Ortho/Para
17.2
FeBr
(cat.)
3
+ Br
(+ HBr)
1
2
(or Fe cat)
Cl
H
Deactivating
Ortho/Para
17.2
AlCl
(cat.)
3
+ Cl
(+ HCl)
2
The halides are unique in being deactivating but ortho/para directing. All other o/p-
directors are activating, and all other deactivating groups are m-directors.
Mech
NO
H
2
Deactivating
Meta
17.3
H
SO
2
4
2
(+ H
O)
+ HNO
2
3
The product can be reduced to Ar-NH
by Fe/HCl or Sn/HCl. Nitration/Reduction
2
provides an effective way to introduce an NH
group. Reduction converts m-directing
2
NO
group into an o/p-directing NH
group.
Mech required.
2
2
Ortho/para
17.10
Activating
H
R
AlCl
(cat.)
3
3
+
R-X
(+ HCl)
a. Restricted to 3º, 2º, or ethyl halides. 1º halides suffer carbocation rearrangements.
b. Since product is more active than starting material, polyalkylation is often a serious
problem.
c. Fails with strongly deactivated benzenes.
Mech required.
O
Deactivating
Meta
17.11
H
O
AlCl
(cat.)
3
R
4
(+ HCl)
+
Cl
R
a. The product can be reduced to -CH
R by Zn(Hg)/HCl.
2
b. The acylation-reduction sequence provides an effective way to introduce a 1º alkyl
group.
c. Reduction converts meta-directing acyl group into an ortho/para-directing alkyl
group.
Mech required.
H
SO
H
3
H
SO
2
4
5
Deactivating
Meta
17.4
+
SO
3
The sulfonyl group is a useful para-blocking group, since it can later be removed upon
+
treatment with H
O/H
.
No mech required.
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10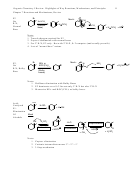 11
11 12
12 13
13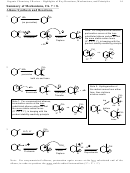 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20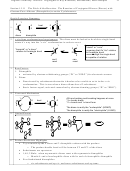 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30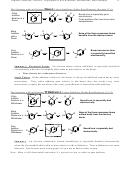 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34