Review Of Organic Chemistry Page 5
ADVERTISEMENT
Organic Chemistry I Review: Highlights of Key Reactions, Mechanisms, and Principles
5
3. Transition-State Stability/Reactivity: The more stable the transition state, the faster the
reaction will be. (The concept here is that the lower the transition state, the more easily it will be
crossed.)
• S
2 Reactivity
N
Br
Br
<
<
<
Br
Br
3°
2°
1°
1° plus allylic
Why: The pattern reflects the relative stability of the transition states. In the case of 3˚ versus 2˚ versus 1˚, the issue is
steric congestion in the transition state. The transition states for the more highly substituted halides are
destabilized. In the case of allylic halides, the transition state is stabilized for orbital reasons, not steric
reasons.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10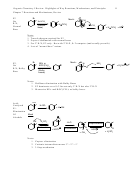 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30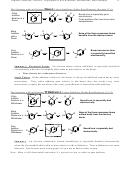 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34