Review Of Organic Chemistry Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
Organic Chemistry I Review: Highlights of Key Reactions, Mechanisms, and Principles
4
2. Product Stability/Reactivity: The more stable the product, the more favorable its formation
will be. In terms of rates, this means that the more stable the product, the faster the reaction.
(The concept here is that the more stable the product, the more favorable it will be to make that
product.)
Key note: Often the “product” that’s relevant in this context will not be the final product of
the reaction, but will be the “product” of the rate determining step.
• Acidity
O
<
<
<
CH
NH
OH
3
2
OH
Why: Because as the stability of the anion products increases from A to D, the reactivity of
the parent acids increase
O
<
<
<
CH
Na
NHNa
ONa
2
ONa
A
C
B
D
• Reactivity of alkanes toward radical halogenation
CH
<
3
<
<
H
C
3
Why: Because as the stability of the radical produced during the rate-determining-step
increases, the reactivity of the parent alkane increases
•
•
<
•
•
<
<
1°
2°
3°
3° plus resonance
• S
1, E1 Reactivity
N
Br
Br
Br
<
<
<
Br
Why: Because as the stability of the cation produced in the rate-determining step increases,
the reactivity of the parent halide increases as well
+
+
<
+
<
<
+
1°
2°
3°
3° plus resonance
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10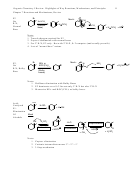 11
11 12
12 13
13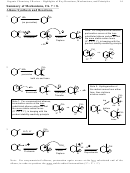 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20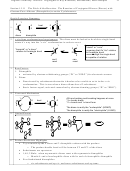 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30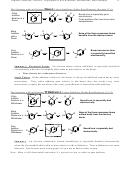 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34