Review Of Organic Chemistry Page 29
ADVERTISEMENT
Organic Chemistry I Review: Highlights of Key Reactions, Mechanisms, and Principles
29
Section 17.1 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
General Mechanism for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
Lewis or protic acid
E-X
E
electrophile formation
E
H
E
H
E
-H
+ resonance structures
deprotonation
electrophile
addition
Three Resonance Structures for Every Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
E
H
E
H
E
H
Additions to Substituted Benzenes. The Effect of Substituents on Reactivity Rates and the Position
of Substitution. (17.4, 5, 6)
Three Issues
1. Activators versus Deactivators
2. Electron Donors versus Electron Withdrawing Groups
3. Ortho-Para directors versus Meta Directors
Fact: The rate determining step is the cation addition step
The transition state much resembles the carbocationic product of that step
What’s good for the cation is good for the reaction rate (product stability-reactivity principle)
Cation stabilizers = electron donors good for cations good for rates = activators
Cation destabilizers = electron withdrawers bad for cations bad for rates = deactivators
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10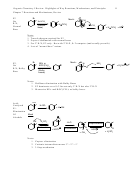 11
11 12
12 13
13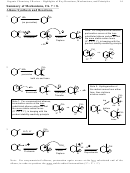 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20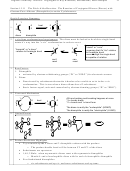 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30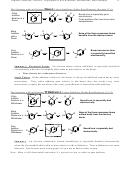 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34