Review Of Organic Chemistry Page 17
ADVERTISEMENT
Organic Chemistry I Review: Highlights of Key Reactions, Mechanisms, and Principles
17
Impact of Conjugation
4. Stability: Conjugation is stabilizing because of p-orbital overlap (Sections 15.2, 4, 7)
• Note: In the allyl family, resonance = conjugation
One p
Two p’s
Three p’s
Four p’s
Six p’s in circuit
Unstabilized
Allyl type
Butadiene type
Aromatic
π-bond
Isolated
C=C
C=O
O
C=N
O
O
O
NH
O
2
OH
O
OR
O
5. Reactivity: Conjugation-induced stability impacts reactivity (Sections 15.4-7)
• If the product of a rate-determining step is stabilized, the reaction rate will go faster
(product stability-reactivity principle)
o Common when allylic cations, radicals, or carbanions are involved
• If the reactant in the rate-determining step is stabilized, the reaction rate will go slower
(reactant stability-reactivity principle)
o Why aromatics are so much less reactive
o Why ester, amide, and acid carbonyls are less electrophilic than aldehydes or ketones
6. Molecular shape (Sections 15.3, 8, 9)
• The p-orbitals must be aligned in parallel for max overlap and max stability
2
• The sp
centers must be coplanar
2
All four sp
carbons must be flat for the p's to align
2
7. Bond Length: Bonds that look like singles but are actually between conjugated sp
centers are
shorter than ordinary single bonds
1.54 A
1.48 A = Shortened
1.33 A
Shortened
Shortened
Shortened
normal
normal
and Strengthened
and Strengthened
and Strengthened
and Strengthened
single
double
conjugated single
NH
O
OR
O
OH
2
O
• In amides, esters, and acids, the bond between the carbonyl and the heteroatom is shortened
•
2
8. Bond Strength: Bonds that look like singles but are actually between conjugated sp
centers
are stronger than ordinary single bonds
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10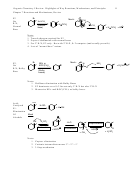 11
11 12
12 13
13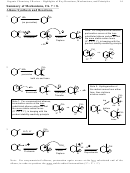 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20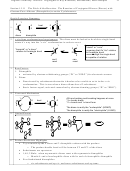 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30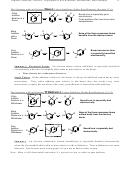 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34