Review Of Organic Chemistry Page 6
ADVERTISEMENT
Organic Chemistry I Review: Highlights of Key Reactions, Mechanisms, and Principles
6
Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 6
Summary of Reaction Types, Ch. 4-6, Test 2
1. Radical Halogenation (Ch. 4)
Br
Br
, hv
2
resonance stabilized>3º>2º>1º>alkenyl
Recognition: X
, hv
2
Predicting product: Identify which carbon could give the most stable radical, and substitute a
Br for an H on that carbon.
Stereochemistry: Leads to racemic, due to achiral radical intermediate.
Mech: Radical. Be able to draw propagation steps.
•
•
Br
Br Br
Br
H
•
+
Br
slow step
ready
to repeat
+ H-Br
first step
2. S
2 Substitution
N
Br
NaOCH
OCH
3
3
S
2: 1º>2º>3º> alkenyl
N
Any of a large variety of nuclophiles or electrophiles can work.
Recognition:
A. Anionic Nucleophile, and
B. 1° or 2º alkyl halide
(3º alkyl halides fail, will give E2 upon treatment with Anionic Nucleophile/Base. For 2º alkyl
halides, S
2 is often accompanied by variable amounts of E2.)
N
Predicting product: Replace the halide with the anion nucleophile
Stereochemistry: Leads to Inversion of Configuration
Mech: Be able to draw completely. Only one concerted step!
Br
OCH
OCH
3
2: 1º>2º>3º> alkenyl
+ Br
3
S
N
3. E2 Reactions.
Br
Br
Mech:
NaOCH
3
+
H OCH
H
3
OCH
3
H
+
H OCH
+ Br
3
E2: 3º>2º>1º> alkenyl
Recognition:
A. Anionic Nucleophile/Base, and
B. 3º or 2º alkyl halide
(1º alkyl halides undergo S
2 instead. For 2º alkyl halides, E2 is often accompanied by variable
N
amounts of S
2.)
N
Orientation: The most substituted alkene forms (unless a bulky base is used, ch. 7)
Predicting product: Remove halide and a hydrogen from the neighboring carbon that can give
the most highly substituted alkene. The hydrogen on the neighboring carbon must be trans,
however.
Stereochemistry: Anti elimination. The hydrogen on the neighbor carbon must be trans/anti.
Mech: Concerted. Uses anion. Be able to draw completely. Only one concerted step!
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10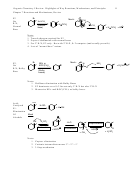 11
11 12
12 13
13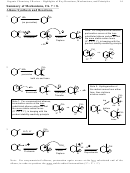 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20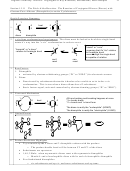 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30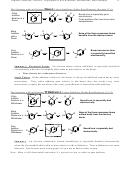 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34