Inventory Control Guide Page 11
ADVERTISEMENT
3.3 EOQ: examples and sensitivity
2OD
EOQ = Q* =
Economic Order Quantity
H
Examples
D
O
H
Q*
M(Q*)
(box/y.)
(
)
/box/y)
(box)
(
)
BEF
(BEF
BEF
cigarettes
365
100
20
60
1208
365
1
20
6
121
milk
365
100
1560
7 10671
365
1
1560
0.7
1067
Here are some numerical examples. Assume you drink one liter milk and you smoke one box
of cigarettes every day. This means a yearly demand of 365 items.
The order cost is 1BEF (you go by foot) or 100 BEF (if you need the car).
The holding cost is 20 percent a year of the money invested in cigarettes. If one item costs
100 BEF, the yearly holding cost for one cigarette box is 20 BEF.
For the milk, one liter which remains one week can be thrown away. It costs thus 30 BEF a
week. This means a yearly holding cost of 1560 BEF.
Sensitivity Analysis
Assume Q instead of Q* is ordered.
The idea is to know how much we loose if we do not order by lots of size EOQ. For example,
how much does it cost more when ordering by 120 when the EOQ is 60.
Here we compare the management costs M(Q) only.
+
M
( )
Q
OD
/
Q
H
Q
/
2
1
Q
*
Q
=
=
+
M
( *)
Q
2
ODH
2
Q
Q
*
If we order by 120(=Q) instead of 60 (=Q*), we pay 1/2(2+0.5)=1.25 times the minimum cost.
In other words, the management costs are increased by 25 %.
Prod 2100-2110
Inventory Control
10
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14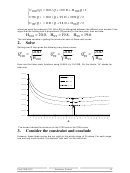 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40








