Inventory Control Guide Page 9
ADVERTISEMENT
EOQ: the solution
The cost over one year when the products are ordered by lots of size Q is given by:
C(Q) =
O D / Q + H Q / 2 + I D
Here is a graphical representation of the two first terms of cost function C(Q). Since the item
cost I D does not depends on Q, it has not been represented.
4000
holding cost
3500
order cost
3000
management cost
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
order quantity Q
Minimize C(Q) over Q
This is a classical minimization problem which can be solved analytically. The solution
consists first in vanishing the first derivative
- O D / (Q*) 2 + H / 2 = 0
C' (Q*) = 0
2OD
Q* =
= EOQ
H
and then, in verifying that the second derivative is positive.
C'' (Q) = 2 O D/ Q 3 > 0
OK
Let us now compute the order and the holding cost for this optimal solution.
H
2OD
H
=
+
+
C
( *)
Q
OD
ID
2OD
H
2
ODH
ODH
=
+
+
+
ID = 2ODH
ID
2
2
We observe that when using the EOQ, the holding cost and the order/setup cost are equal.
This could also be seen on the chart on top of this page.
Holding costs ≈ ≈ ≈ ≈ Order Costs
EOQ:
The EOQ is the value which best compromises the costs of holding items and the costs of
ordering items. This notion of compromise becomes clear by a marginal reasoning.
Prod 2100-2110
Inventory Control
8
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14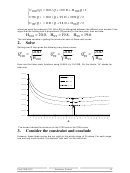 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40








