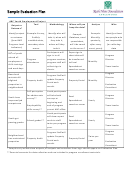
Evaluation Plan Guidance Page 24
ADVERTISEMENT
EVALUATION PLAN GUIDANCE
SOCIAL INNOVATION FUND
If the evaluation plan includes a comparison or control group, the plan should include a way of assessing
whether or not the comparison or control group was in any way exposed to the program components. Ideally,
the plan should include a way of determining the amount the program may have diffused in a given area to
establish how much non-participants may have been exposed to aspects of the program. Include in the plan
ways of estimating differences between program participants and control or comparison group members in
terms of access to program components and delivery of services.
The implementation evaluation plan should include specific measures that will be used to assess how the
program was implemented. The plan should address how data will be collected regarding service provision,
program participants, and the control or comparison group, if applicable. Include specifics about the types of
data to be collected, how they will be collected (such as data collection instruments), and how they will be
analyzed.
Sampling, Measures, and Data Collection
Sampling
Additional Resources
The sampling plan will provide a complete description of who will participate
in the study and how they will be selected. A well thought out sampling plan
More details, and instructions
can help prevent problems with internal and external study validity.
for calculating statistical
power, can be found on the
A power analysis is a calculation that estimates, given a specific sample size
UCLA statistical computing
and analysis design, how likely it is that a program effect will be significant.
software
website:
There are different techniques available for calculating a power analysis, and
exactly which power analysis formula to be used will depend on the details of
ae/
the study, including the amount and types of information collected (the
See Bloom (2005) for more
independent variables), and the desired level of explanation the study hopes
information on sample size
to provide (the size of the expected R-squared). Power analysis calculators for
and MDES in evaluation
different techniques, such as ANOVA and
regression
analyses, are available
research.
online.
A common way of demonstrating statistical power is to provide the calculation of the Minimum Detectable
Effect Size (MDES) that has an 80 percent chance (the conventional level used in evaluation research) of being
statistically significant at a specific level of significance
(alpha
level). The MDES is a calculation designed to
detect the smallest effect statistically notable in the study. MDES calculations help researchers determine if the
findings from a study of a particular sample size are to be believed, statistically speaking. In practice, MDES
helps determine what effect the size of the sample – the number of participants (or groups or sites) – will have
on statistical calculations. It also helps researchers examine if the effects seen in the study group are significant
given the sample size (Bloom, 2005).
Specific Guidance: Sampling Plan and Power Analysis
Sampling Plan
First, describe the population to which the study results will be generalized - that is, the group of individuals
to whom the study results would apply. This might include details such as the social, economic, or
demographic characteristics (race, gender, etc.), at-risk status, or geographic location of the population.
Importantly, the evaluation plan should demonstrate that the sample that will be drawn will be representative
of that population.
nationalservice.gov/SIF
21
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65 66
66 67
67 68
68