Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 11
ADVERTISEMENT
493
13.1 Gases and Their Properties
Explanations for Other Real World Situations
The relationships between gas properties can be used to explain how we breathe in
O
12
bjeCtive
and out. When the muscles of your diaphragm contract, your chest expands, and the
volume of your lungs increases. This change leads to a decrease in the number of
particles per unit volume inside the lungs, leaving fewer particles near any give area
of the inner surface of the lungs. Fewer particles means fewer collisions per second
per unit area of lungs and a decrease in force per unit area, or gas pressure. During
quiet, normal breathing, this increase in volume decreases the pressure in the lungs to
about 0.4 kilopascals lower than the atmospheric pressure. As a result, air moves into
the lungs faster than it moves out, bringing in fresh oxygen. When the muscles relax,
the lungs return to their original, smaller volume, causing the pressure in the lungs to
increase to about 0.4 kilopascals above atmospheric pressure. Air now goes out of the
lungs faster than it comes in (Figure 13.9).
Figure 13.9
O
12
bjeCtive
The Mechanics of Breathing
External
Pressure
101.3 kPa
101.3 kPa
100.9 kPa
101.7 kPa
= 101.3 kPa
Diaphragm
e diaphragm contracts, and the chest
e diaphragm relaxes and the chest
expands, causing the lungs to expand.
returns to its original volume, causing
e increased volume decreases the
the lung volume to decrease.
pressure in the lungs to below the
is increases the pressure in the lungs,
external pressure, causing air to move
causing air to move out of the lungs
into the lungs faster than it moves out.
faster than it moves in.
Let’s return to the gas-related issues discussed at Lilia’s family dinner. When Lilia’s
O
13
bjeCtive
brother John adds helium gas to one of his instrument-carrying balloons, its
volume increases. Increased number of gas particles leads to increased gas pressure,
making the internal pressure greater than the external pressure acting on the outside
surface of the balloon. The increase of internal pressure leads to an expansion of the
balloon. When the balloon is released and rises into the air, the concentration of
gases outside the balloon decreases with increased distance from the earth, leading
to a decrease in the atmospheric pressure acting on the outside of the balloon. The
greater pressure inside the balloon causes the balloon to expand as it rises. This
increase in volume is diminished somewhat by the slight loss of gas from tiny holes
in the balloon and by the general decrease in temperature with increased distance
from the earth.
The volume of this balloon
When the temperature is increased for the gases in the reaction vessel that Lilia’s
will increase as it moves up
sister Rebecca is helping design, the gas pressure rises. This is due to an increase in
into the atmosphere.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4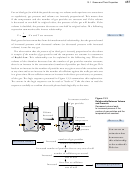 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10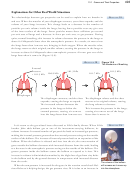 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28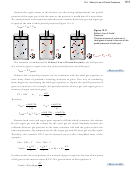 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








