Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 31
ADVERTISEMENT
513
13.4 Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
e
13.10 - Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
xample
If an 85-mL light bulb contains 0.140 grams of argon and 0.011 grams of nitrogen at
O
22
bjeCtive
20 °C, what is the total pressure of the mixture of gases?
Solution
Step 1 Although there are no mass variables in our partial pressure equations, we do
know that we can convert mass to moles using molar masses.
1 mol Ar
= 0.00350 mol Ar
= ? mol Ar = 0.140 g Ar
n
Ar
39.948 g Ar
1 mol N
2
= ? mol N
= 0.011 g N
= 0.00039 mol N
n
2
2
2
N
28.0134 g N
2
2
V = 85 mL
T = 20 °C + 273.15 = 293 K
Step 2 Our variables fit the following form of Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures.
RT
RT
= (Σn
= (n
+ n
P
)
P
)
total
each gas
total
Ar
N
2
V
V
Steps 3-6 We do not need to rearrange the equation algebraically, but when we plug
in our values with their units, we see that we need to convert 85 mL to liters
to get our units to cancel correctly.
0.082058 L atm
(293 K)
3
mL
10
K mol
= (0.00350 mol Ar + 0.00039 mol N
P
)
total
2
85 mL
1 L
= 1.1 atm (or 1.1 × 10
2
kPa)
e
13.5 - Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
xerCise
A typical “neon light” contains neon gas mixed with argon gas.
O
21
bjeCtive
O
22
a. If the total pressure of the mixture of gases is 1.30 kPa and the partial
bjeCtive
pressure of neon gas is 0.27 kPa, what is the partial pressure of the argon
gas?
b. If 6.3 mg of Ar and 1.2 mg Ne are added to a 375-mL tube at 291 K, what
is the total pressure of the gases in millimeters of mercury?
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4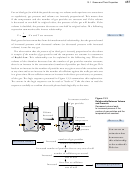 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10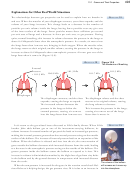 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28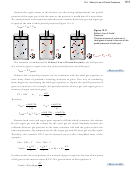 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








