Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 29
ADVERTISEMENT
511
13.4 Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
Because the argon atoms in the mixture are also acting independently, the partial
pressure of the argon gas is also the same as the pressure it would have if it were alone.
The total pressure in the luminous tube that now contains both neon gas and argon gas
is equal to the sum of their partial pressures (Figure 13.11).
= P
+ P
P
total
Ne
Ar
Figure 13.11
Dalton’s Law of Partial
Pressures
The total pressure of a mixture of
ideal gases is equal to the sum of the
partial pressures of each gas.
P
P
A
B
P
= P
+ P
total
A
B
The situation is summarized in Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures: the total pressure
of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of all the gases.
= ΣP
P
O
21
bjeCtive
total
partial
Dalton’s law of partial pressures can be combined with the ideal gas equation to
solve many kinds of problems involving mixtures of gases. One way of combining
them begins by rearranging the ideal gas equation to express the partial pressures of
gases in a mixture—for example, the partial pressures of neon gas and argon gas in a
mixture of argon and neon gases:
P = nRT
PV = nRT
or
V
Therefore,
n
RT
n
RT
Ne
Ne
Ar
Ar
=
=
P
P
Ne
Ar
V
V
Ne
Ar
n
RT
n
RT
Ne
Ne
Ar
Ar
= P
+ P
=
+
P
total
Ne
Ar
V
V
Ne
Ar
Because both neon and argon gases expand to fill the whole container, the volume
for the argon gas and the volume for the neon gas are equal. Similarly, because the
collisions between gas particles in the same container will lead the gases to have the
same temperature, the temperatures for the argon gas and the neon gas are also equal.
Therefore, the common RT/V can be factored out to yield a simplified form of the
equation.
= V
= V
= T
= T
V
T
Ar
Ne
Ar
Ne
n
RT
n
RT
RT
Ne
Ar
=
+
= (n
+ n
P
)
total
Ne
Ar
V
V
V
In other words, the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the moles
of all gases in the mixture times RT/V. The general form of this equation is
RT
O
22
= (Σn
P
)
bjeCtive
total
each gas
V
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4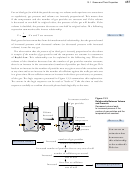 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28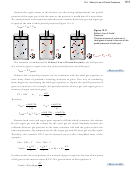 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








