Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 25
ADVERTISEMENT
507
13.3 Equation Stoichiometry and Ideal Gases
Sample Study
T
-
– You are asked to convert an amount of one substance to an amount of
ip
off
another substance, both involved in a chemical reaction.
Sheet 13.3
Equation
G
S
eneral
TepS
Stoichiometry
Step 1 Convert the amount of substance 1 to moles 1.
Problems
For a pure solid or liquid, this will be a molar mass conversion from mass to
moles.
1 mol 1
g 1
(molar mass) g 1
For solutions, molarity can be used to convert from volume of solution to
moles.
(number from molarity) mol 1
L solution 1
1 L solution 1
(number from molarity) mol 1
or
mL solution 1
3
10
mL solution 1
For a gas at STP, the molar volume at STP can be used as a conversion factor to
O
19
bjeCtive
convert from volume of gas at STP to moles.
1 mol 1
L 1
22.414 L 1
For a gas under conditions other than STP, the ideal gas equation can be used
O
19
bjeCtive
to convert volume to moles, or the universal gas constant, R, can be used as a
conversion factor.
P
V
1
1
n
=
1
RT
1
_____ atm
K mol
L 1
or
_____ K
0.082058 L atm
_____ atm
K mol
L 1
or
8.3145 L kPa
_____ K
Step 2 Convert moles of substance 1 to moles of substance 2, using the coefficients
from the balanced equation.
Step 3 Convert moles of substance 2 to amount of substance 2.
For a pure solid or liquid, this will be a molar mass conversion from moles to
mass.
(coefficient 2) mol 2
(molar mass) g 2
(coefficient 1) mol 1
1 mol 2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4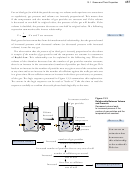 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25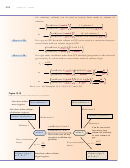 26
26 27
27 28
28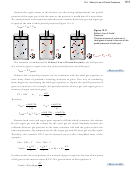 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








