Gases Chemistry Worksheet - Chapter 13, An Introduction To Chemistry Page 5
ADVERTISEMENT
487
13.1 Gases and Their Properties
For an ideal gas (in which the particles occupy no volume and experience no attractions
or repulsions), gas pressure and volume are inversely proportional. This means that
if the temperature and the number of gas particles are constant and if the volume
is decreased to one-half its original value, the pressure of the gas will double. If the
volume is doubled, the pressure decreases to one-half its original value. The following
expression summarizes this inverse relationship:
1
P ∝
O
10
if n and T are constant
bjeCtive
a
V
Real gases deviate somewhat from this mathematical relationship, but the general trend
of increased pressure with decreased volume (or decreased pressure with increased
volume) is true for any gas.
The observation that the pressure of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume
it occupies if the number of gas particles and the temperature are constant is a statement
of Boyle’s Law. This relationship can be explained in the following way. When the
volume of the chamber decreases but the number of gas particles remains constant,
there is an increase in the concentration (number of particles per liter) of the gas. This
leads to an increase in the number of particles near any given area of the container walls
at any time and to an increase in the number of collisions against the walls per unit area
in a given time. More collisions mean an increase in the force per unit area, or pressure,
of the gas. The logic sequence presented in Figure 13.3 summarizes this explanation.
The arrows in the logic sequence can be read as “leads to.” Take the time to read the
sequence carefully to confirm that each phrase leads logically to the next.
Figure 13.3
A constant number
Relationship Between Volume
of gas particles
and Pressure
Decreased volume leads
to increased pressure if the
number of gas particles and the
Volume
temperature are constant.
decreased
Constant
temperature
O
10
bjeCtive
a
Increased
pressure
You can see an
animation that
demonstrates
number of gas particles
this relationship
Increased
Decreased volume
volume of container
at the textbook’s
Web site.
Increased number of particles close to any area of wall
number of collisions per second
Increased
area of wall
force due to collisions
Increased
Increased gas pressure
area of wall
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4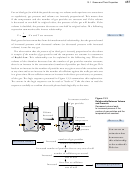 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10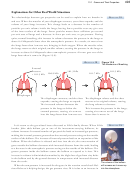 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25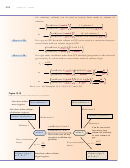 26
26 27
27 28
28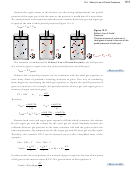 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49








